* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download APES Important Graphics, Charts and Data
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
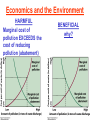
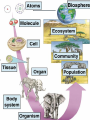
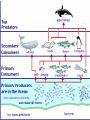
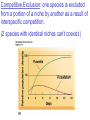
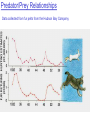
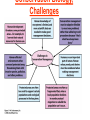
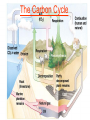
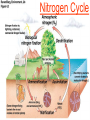
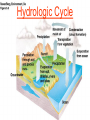
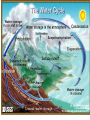
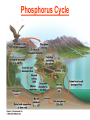
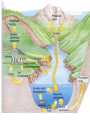
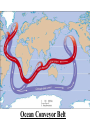
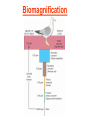
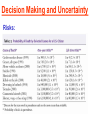
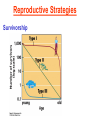
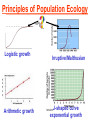
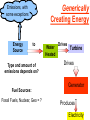
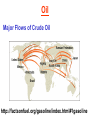
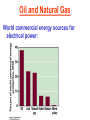
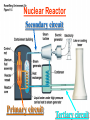
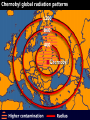
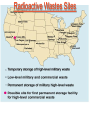
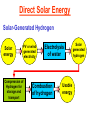
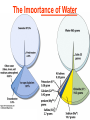
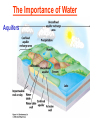
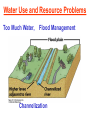
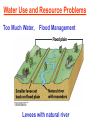
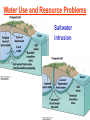
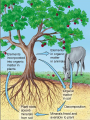
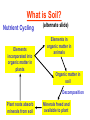
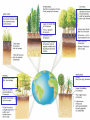
Pretty Pictures for all of the Visual learners Environmental History of U.S. National Environmental Policy Act dictates ALL federally proposed actions draft an environmental impact statement. Carcinogens Carcinogens cancer causing substances See table 2-1 in text. Page 26 Deaths caused by smoking Economics and the Environment Cost-Benefit diagram: economists identify the optimum amount of pollution as the amount at which Marginal costs= marginal cost abatement Economics and the Environment HARMFUL Marginal cost of pollution EXCEEDS the cost of reducing pollution (abatement) BENEFICIAL why? Levels of Biological Organization Antarctic food web Competitive Exclusion: one species is excluded from a portion of a niche by another as a result of interspecific competition. (2 species with identical niches can’t coexist.) Ecological Succession Grasses shrubs poplars (cottonwoods) pine trees oak Predator/Prey Relationships Data collected from fur pelts from the Hudson Bay Company Factors that Affect Population Size Case-in-Point: Predatory Prey Dynamics on Isle Royale Biological Diversity Biodiversity Species Richness Genetic Diversity Ecosystem Diversity Why we need organisms Biological diversity: the number and variety of organisms. Genetic diversity: variation within a species. Species richness: the number of species Ecosystem diversity: variation within an ecosystem. Ecosystem Services and Species Richness Why We Need Organisms Ecosystem Services and Species Richness Nests eventually become small islands of trees Gator trails clear out aquatic vegetation Maintains smaller fish populations by eating gar Digs underwater holes used by other aquatic organisms DDT and the Peregrine Falcon Endangered & threatened Species • What factors are common with most Endangered & threatened species? Gymnogyps californianus Endangered & threatened Species • Endangered & threatened species often have: • Limited natural ranges • Low population densities. • Low reproductive rates • Very specialized nutritional or reproductive requirements. Conservation Biology, Challenges The Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Phosphorus Cycle Atmospheric Circulation Winds: complex horizontal movements of the atmosphere. Ocean Conveyor Belt Climate associated with ENSO Biomagnification Determining Health Effects of Environmental Pollution Lethal Dose-50% (LD50) Determining Health Effects of Environmental Pollution Effective Dose-50% (ED50) – Dose that induces 50% of test subjects to have some type of effect Dose response curve – Decision Making and Uncertainty Risks: Decision Making and Uncertainty Cost-Benefit Analyses Cost Benefit Reproductive Strategies Survivorship Principles of Population Ecology Maximum Population Growthunder ideal conditions = intrinsic rate of increase (aka biotic potential) J-shaped curve (exponential growth) Principles of Population Ecology Logistic growth Arithmetic growth Irruptive/Malthusian J-shaped curve exponential growth Principles of Population Ecology Overshooting the carrying capacity can lead to a population crash. Factors that Affect Population Size Density-Dependence and Boom-or-Bust Population Cycles Demographics of Countries Demographic Stages High avg. # of children born (Baby boom) Demographics of Countries Age Structure of Countries Generalized Age Structure Population and Urbanization Urban migration The City as an Ecosystem Environmental Problems Associated with Urban Areas • Creation of urban heat islands The City as an Ecosystem Environmental Problems Associated with Urban Areas • Dust domes Making Cities More Sustainable What has Curitiba, Brazil done to become a world model for sustainability? Generically Creating Energy Emissions, with some exceptions Energy Source to Type and amount of emissions depends on? Water Heated Drives Turbine Drives Generator Fuel Sources: Fossil Fuels, Nuclear, Geo = ? Produces Electricity Energy Consumption Per capita energy consumption Energy Consumption Energy consumption in the US Coal Making Coal a Cleaner Fuel • Using scrubbers • Using fluidized-bed combustion Oil Major Flows of Crude Oil http://factsonfuel.org/gasoline/index.html#1gasoline Oil and Natural Gas World commercial energy sources for electrical power: Oil and Natural Gas Petroleum refining Oil and Natural Gas Reserves of Natural Gas Oil and Natural Gas Case-in-Point: The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge Synfuels and Other Potential Fossil Fuel Resources Synthetic fuel sources: • Tar sands (oil sands) • Oil shales • Gas hydrates • Coal liquefaction • Coal gasification Problem: these all still produce CO2 Nuclear Fuel Cycle Not taking place Nuclear Fission http://www.atomicarchive.com/Movies/Movies/chainreaction.mov Nuclear Reactor Secondary circuit Primary circuit Tertiary circuit Nuclear Reactors Consist of ... 1 ) Reactor core: Fission takes place heat. 2) Steam Generator: heat from reactor core produces steam. 3) Turbine: steam spins the turbine to generate electricity. 4) Condenser: cools the steam back to liquid water. Chernobyl Exposure to radiation Radioactive Wastes Sites Yucca Mountain 145 km (90) miles from Las Vegas Scientific community agrees that underground repositories are the best long term option of high-level radioactive waste. Around the world there are 2 dozen countries planning similar repositories Direct Solar Energy Heating Buildings and Water, Passive solar heating Direct Solar Energy Heating Buildings and Water Passive solar heating Direct Solar Energy Solar-Generated Hydrogen Solar energy PV or wind generated electricity Compression of Hydrogen for storage and transport Electrolysis of water Combustion of hydrogen Usable energy Solar generated hydrogen Indirect Solar Energy Wind Energy The Importance of Water The Importance of Water Largest watersheds The Importance of Water Aquifers Water Use and Resource Problems Too Much Water, Flood Management Channelization Water Use and Resource Problems Too Much Water, Flood Management Levees with natural river Water Use and Resource Problems Saltwater intrusion Water Management Providing a Sustainable Water Supply Desalinization Condenses Two methods: 1) Distillation Simplified process: Pure water is collected Produces steam Salt water Water boiled Water Conservation Reducing Agricultural Water Waste Reducing Water Waste in Industry Reducing Municipal Water Waste Recycling water Xeriscaping Ecological Succession Pioneer Organisms Climax Community What is Soil? Soil Composition 25% 45% 25% 5% Mineral matter Organic matter Water Air What is Soil? Soil Horizons E-horizon develops if leaching is severe. ? What is Soil? Nutrient Cycling Elements incorporated into organic matter in plants (alternate slide) Elements in organic matter in animals Organic matter in soil Decomposition Plant roots absorb minerals from soil Minerals freed and available to plant Major Soil Types Soil Problems Case-in-Point: The American Dust Bowl Soil Conservation and Regeneration Contour Plowing, Strip Cropping, and Terracing Strip cropping & contour plowing Terracing