* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benthic macroinvertebrates
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
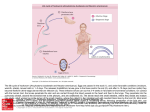
Benthic macroinvertebrates They are ___________ even in the most _________ or environmentally extreme lotic environments contain some ________________ organisms. In general: macroinvertebrates refers to fauna retained by a ___________________. Exception: many early life stages pass through this mesh size (mesh 125-250 um) Macroinvertebrate communities in many lotic environments consists of several _________ species, from numerous phyla: __________: insects, mites, crayfish Molluscs: snails, limpets, mussels, clams ___________: segmented worms Nematodes: roundworms _______________: flatworms Most stream macroinvertebrate species are associated with surfaces of the _________ bottom bedrock, _________ and finer sediments or other stable surfaces (fallen _______, snags, roots, and submerged or emergent aquatic vegetation. (Usually not freeswimming) Collectively called __________________. Fundamental ____ in food web between organic matter resources (leaf litter, algae, detritus) and ________. Aquatic insects Extremely diverse both taxonomically and _______________. Usually the most abundant large organisms collected in stream benthic samples. Thirteen __________ in N. America five are strictly aquatic _________: dragonflys and damselflies Plecoptera: stoneflies ______________: mayflies Trichoptera: caddisflies ____________: hellgrammites Dragonfly, damselfly Stonefly nymphs Stonefly predator Mayfly Larvae Adult mayfly Adult caddis fly Caddis larvae, adult Caddis larvae and cases Caddis larvae and cases Shredders Problems of living in a stream How to obtain ____________? or how to remain in a _______ position? Some lotic species have developed structures to obtain oxygen from the atmosphere (analogous to ______________) Others use temporary storage of an air bubble (analogous to SCUBA diving) A few species use __________________ (analogous to vertebrate hemoglobin) Many have developed _________ gills for obtaining oxygen dissolved in water. Morphological adaptations for existence in running water ____________ projections along trailing edges of legs and body to form hydrofoils that _______ the organism onto the substratum. _______________ of body shape to offer reduced resistance while swimming. ____________ to provide attachment to smooth surfaces. Leg and anal ______ to provide attachment to a variety of surfaces. Life history diversity and adaptability Streams are very dynamic __________ spatially ____________ trophically, etc. Adaptability: 1. Some species are adapted to ___________ streams by having ____________ stages that hatch as they are hydrated when flow resumes. 2. Closely related species that occupy a similar trophic function (or level) may temporally separate growth and _________________ within the same stream reach. 3. ___________ timing of larval __________ (limits _____________ competition by regulating development of young) or ____________ release by adults for mate attraction (synchronizes reproductive behavior with the appearance of young at the time of optimal food availability). 4. Considerable variation in the ______________ cycles to take advantage of resources when plentiful. Some species are multivoltine ____________ univoltine or may require 2 or 3 years to complete life cycle (semivoltine) Life history of a particular species may vary over its’ ____________________. univoltine in a portion of its’ range semivoltine in ________ portion of range. Feeding techniques __________: scraping microbes on solid surfaces. __________ of CPOM Collecting or ___________ of drifting FPOM. Predation Most benthic invertebrates gain little nutritive value from __________ until it has undergone considerable microbial modification (digest ________)