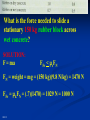* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FRICTION
Contact mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rolling resistance wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Frictional contact mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
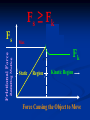
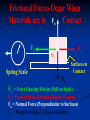
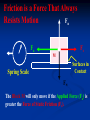
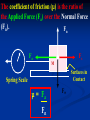
FRICTION - the force that present whenever two surfaces are in contact and always acts opposite to the direction of motion. Depends on: • Type of materials in contact • Surfaces of materials Does NOT depend on: •Surface area in contact •Speed Ff = μFn Ff = Force of Friction in N μ = Coefficient of Friction (depends on material 0<μ<1 Fn = Normal Force; Force acting perpendicular to the two surfaces in contact. In level surfaces, this is equal in magnitude but acting opposite to the weight TYPES OF FRICTION Kinetic Friction - Force needed to keep it going at a constant velocity. Ff = μ kFn Static Friction - Force needed to start motion. Ff < μ sFn Keeps the object at rest. Only relevant when object is stationary. Calculated value is a maximum Fs ≥ Fk Fs Max Fs Fk Static Region Fk Kinetic Region Force Causing the Object to Move Frictional Forces Occur When Materials are in Fn Contact Fa Fs M1 Surfaces in Contact Spring Scale Fw Fa = Force Causing Motion (Pull on Scale) Fs = Force of Static Friction (Resists Motion) Fn = Normal Force (Perpendicular to Surfaces) Fw = Weight of Object ( Mass x Gravity) Friction is a Force That Always Resists Motion Fn Fs Fa M Surfaces in Contact Spring Scale Fw The Block M will only move if the Applied Force (Fa) is greater the Force of Static Friction (Fs). FRICTION converts kinetic energy to heat energy. Banana peel reduces friction. INCREASING FRICTION REDUCING FRICTION The coefficient of friction (μ) is the ratio of the Applied Force (Fa) over the Normal Force (Fn). F n Fs Fa M Surfaces in Contact Spring Scale μ = Fa Fn Fw Determine the amount of force needed to move 12.0 kg of rubber at a constant velocity across dry concrete? Solution: F = ma FFr = μkFN FN = weight = mg = (12 kg)(9.8 N/kg) = 117.6 N FFr = μkFN = (0.8)(117.6 N) = 94.08 N = 90 N 90 N What is the force needed to slide a stationary 150 kg rubber block across wet concrete? SOLUTION: F = ma FFr < μsFN FN = weight = mg = (150 kg)(9.8 N/kg) = 1470 N FFr = μkFN = (.7)(1470) = 1029 N = 1000 N 1000 N Given the following : μs = .62, μk = .48 Determine the acceleration of a sliding 8.50 kg block if a force of 72 N is applied to it? v FFr 72 N 8.5 kg FFr = μkFN FN = mg FFr = μkmg FFr = (.48)(8.5 kg)(9.8 N/kg) = 39.984 N F = ma <72 N - 39.984 N> = (8.5 kg)a, a = 3.77 = 3.8 m/s2 3.8 m/s/s