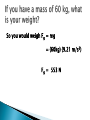* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download gravity ppt - District 196
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Roche limit wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Newton believed that every object ___attracts_____ every other object. The force of the attraction depends on the __mass___ and _distance__ of the two objects. Fg = G (m1m2) r2 Fg = gravitational force in (N) m1 = mass object 1 (kg) m2 = mass object 2 (kg) r = the distance between the masses (m) (measured from their centers) G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2 (a constant everywhere!) Ex. 1 Are you attracted to the person sitting next to you? Calculate the gravitational force between you (mass 70kg) and the person next to you (mass 65kg) if you are 1.2 m apart. Given: m1 = 70 kg m2 = 65 kg r = 1.2 m G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2 Unknown: Fg Equation: Fg = G (m1m2) r2 = (6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2)(70 kg)(65 kg) (1.2 m)2 = 2.11 x 10-7 N = 0.000000211 N (tiny!) As you go further away from the earth’s surface the acceleration due to gravity _decreases____. Two equations for gravitational force F = ma becomes Fg = mg and Fg = G (m1m2) r2 We can set them equal to each other: cancels Fg = Fg mg = G m1 m2 r2 g=Gm r2 one of the masses g = the acceleration due to gravity (m/s2) G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2 m = the mass of the planet in kg r = the distance from the center of the planet in (m) Remember- r measures from CENTER of planet, not the surface. Ex. 2 Find the gravity if you are 2.1 x 10 5 m above the earth’s surface. Given: r = 2.1 x 105 m + 6.37 x 106 m = 6.58 x 106 m mearth = 5.98 x 1024 kg Unknown: Fg Equation: F = ma, now Fg = mg (We need g at that altitude.) Fg = Fg mg = G m1 m2 r2 g=Gm r2 = (6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2)(5.98 x 1024 kg) (6.58 x 106 m)2 = 9.21 m/s2 So you would weigh Fg = mg = (60kg) (9.21 m/s2) Fg = 553 N A geosynchronous satellite orbits above the same point on the equator of the earth at all times. Examples: GPS cell phone satellites TV satellites Satellites are _____projectiles_____. In order to not fall back to earth, they need to maintain a certain velocity… In order for a satellite to stay in a consistent orbit gravitational force = centripetal force Fg= Fc mg = m v2 r (The mass of the satellite cancels out!) g= v2 r g = the acceleration due to gravity in m/s 2 v = the speed of the satellite in m/s r = the distance from the center of the planet in meters Ex. 3 Calculate the speed needed for one of the Direct TV satellites to orbit at an altitude of 320,000 m above the earth’s surface. Given: r = 320,000 m + 6.37 x 106 m = 6,690,000 m or 6.69 x 106 m Unknown: v Equation: Fg = Fc mg = mv2 r g = v2 r We need g at that altitude: Fg = F g mg = G m1 m2 r2 g=Gm r2 = (6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2)(5.98 x 1024 kg) (6.69 x 106 m)2 g = 8.91 m/s2 8.91 m/s2 = ___v2__ (6.69 x 106 m) v = 7,721 m/s (that’s about 17,000 mph!)