* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 9
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
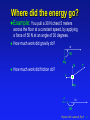
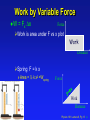
Exam 2 Physics 101: Lecture 9 Work and Kinetic Energy Hour Exam 1, Tomorrow! – Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 1 Energy (and mass) is Conserved Energy is “Conserved” meaning it can not be created nor destroyed Can change form Can be transferred Total Energy does not change with time. This is a BIG deal! Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 2 10 Energy Forms Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Heat Mass (E=mc2) Units Motion (Today) Stored (Thursday) later p102 Joules = kg m2 / s2 Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 3 12 Work: Energy Transfer due to Force Force to lift trunk at constant speed Case a Ta – mg = 0 T = mg Case b 2Tb - mg =0 or T = ½ mg But in case b, trunk only moves ½ distance you pull rope. F * distance is same in both! Ta Tb Tb W = F dcos(q) mg mg Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 4 15 Work by Constant Force A) W>0 B) W=0 C) W<0 Only component of force parallel to direction of motion does work! W = F Dr cos q F 1) Dr F 2) Dr F 3) 4) Dr Dr F Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 5 18 Work by Constant Force Example: You pull a 30 N chest 5 meters across the floor at a constant speed by applying a force of 50 N at an angle of 30 degrees. How much work is done by the 50 N force? N T f mg 50 N 30 Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 7 21 Where did the energy go? Example: You pull a 30 N chest 5 meters across the floor at a constant speed, by applying a force of 50 N at an angle of 30 degrees. How much work did gravity do? Dr 90 mg N How much work did friction do? T f mg f Dr 180 Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 8 25 Kinetic Energy: Motion Apply constant force along x-direction to a point particle m. 1 2 2 recall : ax Dx (vx vx 0 ) 2 Work changes ½ m v2 Define W=DK Kinetic Energy K = ½ m v2 For Point Particles Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 9 35 Example: Block w/ friction A block is sliding on a surface with an initial speed of 5 m/s. If the coefficent of kinetic friction between the block and table is 0.4, how far does the block travel before y stopping? N Y direction: F=ma f x mg W=DK Work 5 m/s Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 10 44 Falling Ball Example Ball falls a distance 5 meters, What is final speed? Only force/work done is gravity mg Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 11 Example: block on incline A 5kg block is at rest on a frictionless incline. It is pulled 4.5m by a 25N force. What is the final velocity of the block? 25N 5kg 30o Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 12 Work by Variable Force W = Fx Dx Force Work is area under F vs x plot Work Distance Spring F = k x » Area = ½ k x2 =Wspring Force Work Distance Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 13 48 Summary Energy is Conserved Work = transfer of energy using force Can be positive, negative or zero W = F d cos(q) Kinetic Energy (Motion) K = ½ m v2 Work = Change in Kinetic Energy S W = DK Physics 101: Lecture 9, Pg 14 50