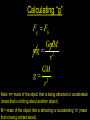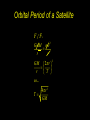* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Universal Law of Gravitation
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
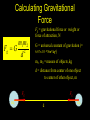
Universal Law of Gravitation Every object attracts every other object with a force that is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Calculating Gravitational Force Fg = gravitational force or weight or force of attraction, N m1m2 Fg G 2 d G = universal constant of gravitation (= 6.67 x 10 -11Nm2/kg2) m1, m2 = masses of objects, kg d = distance from center of one object to center of other object, m Fg m1 Fg d m2 Calculating “g” Fc m Fg Fg •FG GmM mg 2 r GM g 2 r Note: m= mass of the object that is being attracted or accelerated (mass that is orbiting about another object) M = mass of the object that is attracting or accelerating ‘m’ (mass that is being orbited about) Orbital Velocity for a Satellite moving in a Circular Orbit Centripetal Force = Gravitational Force Fc Fg v mv 2 Mm G 2 r r so... v GM r Another Formula for Orbital Speed Fc = Fg mv2 mg r v= rg Note: You must know g to use this equation for v! Orbital Period of a Satellite F gF c GmM mv 2 2 r r GM 2 r r T so... 4 r 3 T GM 2 Useful Constants • • • • • G = 6.67 x 10 -11 N m2/ kg2 Mass of Earth = 5.98 x1024 kg Radius of Earth = 6.37 x 106 m Earth’s orbital radius = 1 A.U. Earth’s orbital period = 1 year