* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces in Two Dimensions Section 7.1
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Statistical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Virtual work wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic system wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
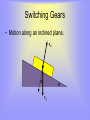
Forces in Two Dimensions Section 7.1 Physics Objectives • Determine the force that produces equilibrium when three forces act on an object. • Analyze the motion of an object on an inclined plane with and without friction. How have we looked at forces in two dimensions? • Friction acting on a crate sliding on the ground. • What angle are these two forces in relation to each other? – 90° – We will now examine forces at other angles to each other in two dimensions. Equilibrium and the Equilibrant • Equilibrium: the net force on an object is zero. • When in equilibrium, the object is either motionless or moves with constant velocity. Equilibrium and Equilibrant • How do we add two vectors? B A C A B C Because they form a closed triangle, the net force = 0. Equilibrium and Equilibrant • We can move vectors around as long as we don’t change the direction (angle) or magnitude. • Suppose we only have two forces that do not add up to zero. • How do we find the third force that, when added to the other two, would add up to zero? Equilibrium and Equilibrant • The force that results in the net force of zero is known as the equilibrant. B R B A A Equilibrant B A R Net Force = 0 Practice Problem • Pg 151 • 2-4 Switching Gears • Motion along an inclined plane. FN Θ Θ Fg Practice Problems • Pg 154 • 5-8





















![[A, 8-9]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006655537_1-7e8069f13791f08c2f696cc5adb95462-150x150.png)