* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MECN 4600 Inter
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Grand canonical ensemble wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
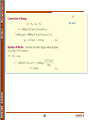
Lecture 6 Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Dynamics MECN 3010 Department of Mechanical Engineering Inter American University of Puerto Rico Bayamon Campus Dr. Omar E. Meza Castillo [email protected] http://www.bc.inter.edu/facultad/omeza Inter - Bayamon Tentative Lecture Schedule Topic Lecture Kinematics of a Particle 1,2,3,4 Kinetics of a Particle: Force and Acceleration 5 Kinetics of a Particle: Work and Energy 6 Kinetics of a Particle: Impulse and Momentum MECN 4600 Planar Kinematics of a Rigid Body 2 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon "Lo peor es educar por métodos basados en el temor, la fuerza, la autoridad, porque se destruye la sinceridad y la confianza, y sólo se consigue una falsa sumisión” Einstein Albert Topic 3: Kinetics of a particle MECN 4600 Work and Energy 3 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Chapter Objectives To develop the principle of work and energy and apply it to solve problems that involve force, velocity, and displacement. To study problems that involve power and efficiency. To introduce the concept of a conservative force and apply the theorem of conservation of energy to solve kinetic problems. 4 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Work of a Force Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Work of a Force Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Work of a Force Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Work of a Force Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Work of a Force Work of a Constant Force Moving Along a Straight Line Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Work of a Force Work of a Weight Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Work of a Force Work of a Spring Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Work of a Force Lecture 6 MECN 4600 13 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 14 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 15 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Principle of Work and Energy Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Principle of Work and Energy Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Principle of Work and Energy for a System of Particles Work of Friction Caused by Sliding Lecture 6 MECN 4600 19 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 20 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 21 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 22 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 23 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 24 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 25 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 26 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 27 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Power and Efficiency Power Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon Power and Efficiency Efficiency MECN 4600 The mechanical efficiency is always less than 1 Lecture 6 MECN 4600 30 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 31 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 32 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 33 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 34 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Conservative Forces and Potential Energy Conservative Force: It is defined by the work done in moving a particle from one point to another that is independent of the path followed by the particle. Two examples are weight of the particle and elastic force of the spring. Potential Energy: It is the measure of the amount of work a conservative force will do when it moves from a given position to the datum. Gravitational Potential Energy: If a particle is located a distance y above an arbitrary selected datum, the particle’s weight W has positive gravitational potential energy V g. Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Conservative Forces and Potential Energy W has the capacity of doing positive work when the particle is moved back down to the datum. The particle is located a distance y below the datum, Vg is negative since the weight does negative work when the particle is moved back up to the datum. If y is positive upward, gravitational potential energy of the particle of weight W is Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Conservative Forces and Potential Energy Elastic Potential Energy: When an elastic spring is elongated or compressed a distance s from its unstretched position, the elastic potential energy Ve can be expressed. Ve is always positive since, in the deformed position, the force of the spring has the capacity for always doing positive work on the particle when the spring is returned to its unstretched position. Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Conservative Forces and Potential Energy Potential Function: If a particle is subjected to both gravitational and elastic forces, the particle’s potential energy can be expressed as a potential function. Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon Conservative of Energy Potential Function: When a particle is acted upon by a system of both conservative and non-conservative forces, the portion of the work done by the conservative forces can be written in terms of the difference in their potential energies using. MECN 4600 As a result, the principle of work and energy can be written as represent the work of the nonconservative forces acting on the particles. Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon Conservative of Energy If only conservative forces are applied to the body, this term is zero and we have MECN 4600 This equation referred to as the conservation of mechanical energy or simply the conservation of energy. It states that during the motion the sum of the particle’s kinetic and potential energies remain constant. Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon Conservative of Energy System of Particles: If a system of particles is subjected only to conservative forces, then an equation can be written. MECN 4600 The sum of the particle’s initial kinetic and potential energies is equal to the sum of the particle’s final kinetic and potential energies. Lecture 6 MECN 4600 42 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 43 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 44 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 45 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 46 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 47 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 48 Lecture 6 Inter - Bayamon Inter - Bayamon MECN 4600 Homework5 WebPage Omar E. Meza Castillo Ph.D. 49 Lecture 6