* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Force Diagrams
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
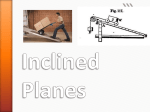
Force Diagrams And Types of Forces Review • Force = push or pull. • Measured in Newtons. – 1 lb = 4.45 N • • • • • Fnet = ma a = Fnet / m Big force = big acceleration Big mass = small acceleration An object’s motion is constant UNLESS a force is applied. – Constant velocity = NO NET FORCE! Types of Forces • Two general classes of force: – Contact forces – Action-at-a-distance forces • Some contact forces – – – – – – friction, Ff tension, Ft normal force, FN drag (air resistance), Fd applied force, Fa spring force, Fs • Some action-at-a-distance forces – gravitational force (weight), Fg or Fw – electric force, FE – magnetic force, FM Weight • Weight is the force exerted on an object by gravity. • Weight = mass x gravity – Fw = mg – Always oriented downward • On Earth, g = 9.81 m/s2 – Weight changes based on location. Weight of a 50-kg Mass on Selected Bodies Location g (m/s2) x Earth Weight (N) Weight (lb) Sun 266 27.1 13,300 2980 Mercury 3.73 0.380 185 41.6 Venus 8.90 0.907 445 99.9 Earth 9.81 1.00 491 110. Moon 1.62 0.165 81.4 18.2 Mars 3.70 0.377 185 41.5 Jupiter (cloudtops) 23.3 2.38 1160 261 Saturn (cloudtops) 10.4 1.06 522 117 Pluto 0.651 0.0664 32.8 7.30 Normal Force • Normal force – exerted by a surface against an object resting on that surface. – Always perpendicular to surface. – “Normal” means “perpendicular”. FN FN Fw Fw Normal Force • On a horiz. surface, FN = Fw • On a slanted surface, FN = Fw cos = mg cos – = angle of incline • What is the weight and normal force for a box sitting on a 15º incline if the box’s mass is 150. kg? – Fw = mg • Fw = (150. kg)(9.81 m/s2) • Fw = 1470 N – FN = Fw cos • FN = (1470 N)(cos15º) • FN = 1420 N Weight vs. Normal Force FN Fw = mg Force Diagram • AKA free-body diagram. • Shows all forces acting on an object. – If you can’t draw, don’t worry! – Usu. represent objects as boxes or circles for simplicity. • Forces drawn as vector arrows. – Bigger arrows for bigger forces. – Only draw forces that are known or requested. – Other forces may exist but aren’t important to the problem. • Label force arrows. Draw a Force Diagram • A box is resting on a horizontal surface. • A box is sliding at constant speed across a horizontal surface. • A box is hanging from a cable. • A box is hanging from two cables that form an angle of 45º. • A box is being pulled along a horizontal plane by a rope that forms an angle of 45º with the floor. • A box is sliding down a frictionless ramp. • A box is sliding down a ramp with friction.