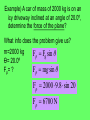* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 24 newtons laws of motion 2 - lindsey
Survey
Document related concepts
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
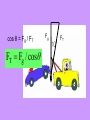
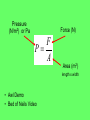
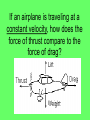
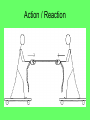
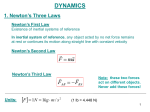
Newton’s Laws Take 2 take out your 3s February 13, 2009 Newton’s 2nd Law proves that different masses accelerate to the earth at the same rate, but with different forces. • We know that objects with different masses accelerate to the ground at the same rate. • However, because of the 2nd Law we know that they don’t hit the ground with the same force. F = ma F = ma 98 N = 10 kg x 9.8 m/s/s 9.8 N = 1 kg x 9.8 m/s/s Terminal Velocity – force of friction = force of gravity air resistance = weight – acceleration = 0 m/s2 – Fnet = 0 N Who has a higher terminal velocity, a person who has a mass of 200 kg or a person with a mass of 100 kg? 200 kg Video Clip • fastest-growing sport in Norway • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nf2ENQ RHKA4 Free Body Diagrams - A picture that shows all of the forces acting on an object What are the forces acting on this object? http://lectureonline.cl.msu.edu/~mmp/applist/si/plane.htm Fn Ff Fp Fg Forces on an inclined plane… Fg mg Fn Fg cos θ Fn Fg Fp Fp Fg sin θ Ff Fn Billy and his dad are sledding down the hill at an angle of 15.0°. If their combined mass is 55.2 kg, what is the force pulling them down the hill? Fp Fg sin θ Fp mg sin θ Fp 55.2 9.8 sin 15 Fp 140 N Example) A car of mass of 2000 kg is on an icy driveway inclined at an angle of 20.0º, determine the force of the plane? What info does the problem give us? m=2000 kg Fp Fg sin θ Ө= 20.0º Fp= ? Fp mg sin θ Fp 2000 9.8 sin 20 Fp 6700 N Tension = stretching force in a rope Demos with spring scales The tension in the rope can be broken down into its horizontal and vertical components. The vertical component of Ft has to equal the Fg. cos θ = Fg / FT FT Fg / cos θ Fg FT Tension Practice Problem • A stop light with a mass of 25 kg is supported by 2 wires. What is the tension in the wire that is 15˚ from the normal? What is the tension in the wire that is 50˚ from the normal? 15˚ 50˚ Tension Practice Problem • A stop light with a mass of 25 kg is supported by 2 wires. What is the tension in the wire that is 15˚ from the normal? What is the tension in the wire that is 50˚ from the normal? 15˚ 50˚ Fg = m g Fg = (25 kg) (9.8 m/s2) = 245 N F t F t 245 N cos 15 253.6 N F t F t 245 N cos 50 381.2 N Pressure (N/m2) or Pa Force (N) F P A Area (m2) length x width • Awl Demo • Bed of Nails Video • Bernoulli's Principle states that as the speed of a moving fluid increases, the pressure within the fluid decreases • Pipe Demo • 2 Hole Water Demo Creates the ability for planes to fly! If an airplane is traveling at a constant velocity, how does the force of thrust compare to the force of drag? Newton’s 3rd Law For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. What forces are involved in a tug of war? Fn Fp Ff Fg Action / Reaction Arnold Strongman and Suzie Small are having a tug of war contest. They pull on opposite ends of a rope. Who exerts a greater force on the rope? • Rope tension must be the same throughout the whole rope. Therefore, Arnold can pull no harder on the rope than Suzie. • The most important factor in a tug of war is not how hard you pull on the rope, but how hard you push on the ground. Suppose two carts, one twice as massive as the other, fly apart when the compressed spring that joins them is released. 1. How does the force exerted by the spring on the 1m-cart compare to the force exerted by the spring on the 2m-cart? The forces are equal 2. How fast does the 2m-cart roll compared to the smaller 1mcart? It would roll half-as fast since it experienced half the acceleration when released from the spring. Which will experience the greater acceleration, the car or truck if the forces are equal? F=F M a =M a Action / Reaction Fgun = Fbullet M a =M a What gun and bullet would you want to be shot with? – A gun with very little mass and a bullet with a lot of mass? Or – A gun with lots of mass and bullet with very little mass? •Fan cart demo •Fire extinguisher DVD demo Reminders • POTW • Work on 35s Newton’s Laws worksheet #2 • No school Monday Hundreds Gather to Protest Global Warming