* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Centripetal Force
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Proper acceleration wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
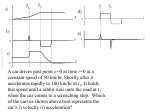
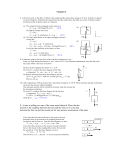
Centripetal Force Acceleration in a Circle v2 dq dv v1 Acceleration is a vector change in velocity compared to time. For small angle changes the acceleration vector points directly inward. This is called centripetal acceleration. a Centripetal Acceleration Uniform circular motion takes place with a constant speed but changing velocity direction. The acceleration always is directed toward the center of the circle and has a constant magnitude. v2 ar 2r r Buzz Saw A circular saw is designed with teeth that will move at 40. m/s. • r = v2/a. The bonds that hold the cutting tips can withstand a maximum acceleration of 2.0 x 104 m/s2. Start with a = v2/r. Substitute values: • • Find the diameter: • Find the maximum diameter of the blade. r = (40. m/s)2/(2.0 x 104 m/s2) r = 0.080 m. d = 0.16 m = 16 cm. Law of Acceleration in Circles Motion in a circle has a centripetal acceleration. There must be a centripetal force. • Vector points to the center F a mv2 Fr m 2 r r The centrifugal force that we describe is just inertia. • It points in the opposite direction – to the outside • It isn’t a real force Conical Pendulum A 200. g mass hung is from a 50. cm string as a conical pendulum. The period of the pendulum in a perfect circle is 1.4 s. What is the angle of the pendulum? What is the tension on the string? q FT Radial Net Force The mass has a downward gravitational force, -mg. There is tension in the string. • The vertical component must cancel gravity FTy = mg FT = mg / cos q FTr = mg sin q / cos q = mg tan q This is the net radial force – the centripetal force. q FT FT cos q FT sin q mg Acceleration to Velocity The acceleration and velocity on a circular path are related. a F / m g tan q a v2 / r v 2 gr tan q v gr tan q q FT r mg tan q mg Period of Revolution The pendulum period is related to the speed and radius. r L sin q q L v 2r / T 2L sin q / T v 2 gr tan q 4 L sin q / T gL sin q sin q / cosq 2 2 2 2 cos q = 0.973 q = 13° r 2 cosq T g / 4 L 2 FT mg tan q Radial Tension The tension on the string can be found using the angle and mass. FT = mg / cos q = 2.0 N If the tension is too high the string will break! next