* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Compressed air energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
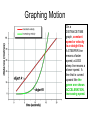
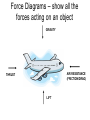
STUDY ISLAND MCAS REVIEW PHYSICAL SCIENCE Assignment #8 Motions of Objects, Heat Energy What is MOTION? An object is in motion if its position changes relative to a reference point (a non-moving object). The observed motion changes when the reference point changes. DESCRIBING MOTION Do you remember these words? ACCELERATION is the Speed rate of change in velocity VELOCITY is the – that means EITHER a speed of an object Velocity change in speed OR a in a given direction change in direction per unit of time. Acceleration SPEED is a rate – how much distance is covered per unit of time Speed = distance ÷ time The car is traveling at 100 miles per hour. It is usually calculated as an AVERAGE speed for a trip = TOTAL distance ÷ TOTAL time Acceleration = (Final velocity – Initial velocity) ÷ time C. Average Speed = total distance ÷ total time: 3m ÷ 6s = 0.5m/s An escalator at a shopping mall is 10 m long and moves at a constant speed of 0.5 m/s. If Jose steps onto the escalator at the bottom while it is moving, how long will it take him to travel the 10m? A. 5 s B. 10 s C. 15 s D. 20 s Graphing Motion On a DISTANCE/TIME graph, constant speed or velocity is a straight line. A STEEPER line means a faster speed; a LESS steep line means a slower speed. A line that is curved upward like the green one shows ACCELERATION, increasing speed. D. Bicyclist U as his motion is the only one with a straight line. The force of GRAVITY All objects in the universe exert a gravitational pull on every other object. Objects with MORE MASS have MORE GRAVITY. Objects that are closer exert more gravitational force as well. Earth is so much more MASSIVE than any other object on earth that its gravitational pull is what we observe when objects fall. Do you remember the difference between mass and weight? MASS is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and doesn’t change from place to place in the universe. WEIGHT is the measurement of the gravitational pull on an object, so it will change if the force of gravity changes. Newton’s Laws of Motion 1st Law: INERTIA – an object at rest stays at rest, or an object moving at constant speed and direction stays moving unless an unbalanced force acts on it to change its motion. 2nd Law: F=ma – force = mass x acceleration. If you throw a ball harder (more force), it will accelerate faster and go farther. 3rd Law: Action – Reaction. One object exerts a force on a 2nd object (action), and the 2nd exerts an equal and opposite force back on the 1st (reaction). Force Diagrams – show all the forces acting on an object GRAVITY AIR RESISTANCE (FRICTION/DRAG) THRUST LIFT HEAT energy, also called THERMAL energy is an example of KINETIC energy – do you remember the difference between POTENTIAL and KINETIC energy??? • Potential energy is stored energy or energy of position, while KINETIC energy is energy of motion – the vibrating motion of molecules in a substance. TEMPERATURE is the average kinetic energy of all the molecules in a substance, where HEAT is the total kinetic energy. Temp = 90°C Temp = 90°C Mass = 50g Mass = 500g The cup on the left has the SAME TEMPERATURE as the pan on the right, but the amount of HEAT on the left is LESS as there are fewer molecules of water. Heat TRANSFER is a one-way road! Warmer things always transfer their heat to cooler things. Cold things DO NOT transfer their coldness – they GAIN heat from something warmer, while the warm object loses heat. Heat is transferred by: CONDUCTION By touch – one particle bumps into or touches another CONVECTION Heat RISES as density is lower, and colder substances sink OR… RADIATION Heat travels across space in waves INSULATORS help PREVENT or SLOW heat transfer – like insulation in your home, a thermos or a cooler