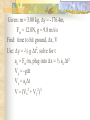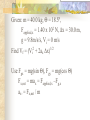* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Force
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
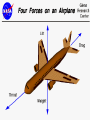
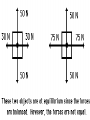
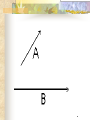
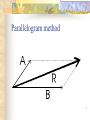
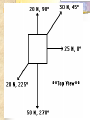
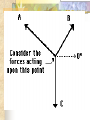
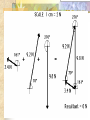
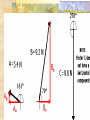
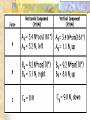
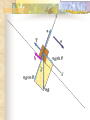
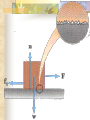
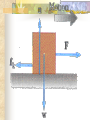
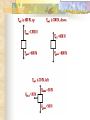
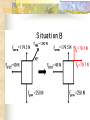
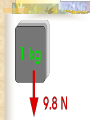
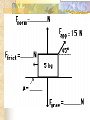
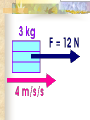
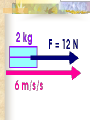
Forces and the Laws of Motion Newton’s Laws: Chapter 4 Buoyant Force: Chapter 9.1 Quiz Given: Force of 30N, east Force of 40N, north Find: resultant force: magnitude and direction Changes in Motion Force: a push or a pull A push or pull changes the velocity of an object whether at rest or moving Force increases directly as the mass of an object increases Force increases directly as an object accelerates to a higher speed In other words, Force = mass x acceleration SI unit for Force Force = mass (kg) x acceleration(m/s2) = kg m/s2 = Newton (N) Or Force = mass (g) x acceleration (cm/s2) = g cm/s2) = dyne 1lb. = 4.448N 1N = 0.225 lb. Classes of Forces Contact force: results from physical contact between two objects Field force: does not require physical contact: ex: gravity, electrical charges Force: a push or a pull Force Diagrams Try this one, part of homework 1. You are walking to class at a constant velocity. To move forward at 0 degrees you push back at 180 degrees with a force of 15N. If you weigh 600N (140lbs) draw a vector diagram of the forces acting on your body as you walk. If Forces are balanced Head to Tail Method Parallelogram method Try this one: also part of homework Given 3 vectors Vector A: 15N at 70 degrees Vector B: 20N at 150 degrees Vector C: 4kg at 270 degrees Diagram it and determine the resultant force by finding the horizontal and vertical components Everyday Forces: Chapter 4-4 1. 2. Weight = Fg = mg = kg x 9.8m/s2 on earth Normal force = Fnorm = Fn = opposite in direction to contact surface = mgcosΘ where Θ is the angle between the normal force and the vertical line. Practice: Solve the following Mr. Trotts is standing on a ramp that has a 15 degree slope to the ground. If Mr. Trotts weighs 100kg what is the normal force acting on him. The Force of Friction Static friction:(Fs) a force resisting objects at rest from moving by opposing forces applied attempting to set them in motion Fs = -Fapplied Kinetic friction:(Fk) retarding frictional force on an object in motion Net external force: force causing object to change motion = F – Fk Coefficient of friction (µ) expresses the dependence of frictional forces on the particular surface they are in contact with Coefficient of kinetic friction: µk = Fk/Fn Fn = mgcosΘ Coefficient of static friction: µs = Fsmax/Fn Force of friction: Ff = µ Fn Try another one: part of homework Practice 4C page 145 #2 (use sample 4C) Net Force Forces up should equal forces down if no change in motion occurs up or down 69.3N right minus 40N left = 29.3N right If the object weighs 100N then its mass is weight/gravity = 100N/9.8m/s/s =about 10kg Acceleration = F/m = 29.3N/10kg = 2.93m/s/s to the right Let’s Practice Practice: Try this one on Three forces are acting on an object. 1. 15N at 90degrees 2. 25N at 220degrees 3. 20N at 300degrees Find the x and y components of each Find the object’s mass assuming no up or down motion Calculate the net force acting on the object Fnet = ΣF = ma Practice: given a net force of 5N to the left acting on a 20kg force find the objects rate of acceleration a= F/m Try yet another: part of homework Given: forces acting on an object 40N at 60 degrees 35N at 170 degrees Object weighs 100kg, Ff = 2N Find: Fg, Fn, Fnet, µ, and the acceleration of the object Quiz: Forces & friction Given Fapplied = 125N 30º above the horizontal East, mass = 250 kg, and Ff = 25N Find: Fg, Fn, µ, and a Let’s mix it up Given m=1.5x107 kg, F=7.5x105 N, Vi = 0, Vf = 85 km/h Find time to increase speed from Vi to Vf Use a = F/m, solve a = Vf – Vi /t for time Given: m = 3.00 kg, Δy = -176.4m, Fw = 12.0N, g = 9.8 m/s/s Find: time to hit ground, Δx, V Use: Δy = -½ g Δt2, solve for t ax = Fw/m, plug into Δx = ½ ax Δt2 Vy = -gΔt Vx = axΔt V = (Vx2 + Vy2)½ Given: m = 40.0 kg, Θ = 18.5º, Fapplied,x = 1.40 x 102 N, Δx = 30.0 m, g = 9.8m/s/s, Vi = 0 m/s Find Vf = (Vi2 + 2ax Δx)1/2 Use Fgx = mg(sin Θ), Fgy = mg(cos Θ) Fx,net = max = Fapplied,x –Fg,x ax- = Fx,net / m Quiz: Putting it together A 250 kg box is pulled along a horizontal surface. A rope attached to the box pulls the box east with a force of 125N at an angle of 25degrees above the horizontal. The force of friction acts with a force of 30N opposite the direction of the box. What is the coefficient of friction and acceleration of the box? Buoyant force Fluids: matter that flows (liquids or gases) -liquid: has volume and takes the shape of its container. -gas: has no shape and fills its container Mass density (ρ) = mass (kg)/volume(m3) Buoyant force: upward force exerted on an object buy the fluid it is immersed in. Apparent weight: the weight of an object immersed in a fluid. Magnitude of buoyant force: (Archimedes principle) any object partially or completely immersed in a liquid experiences an upward buoyant force equal in magnitude to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Buoyant force (FB) = Fg (displaced fluid) = mfg Buoyant force on floating object = weight of floating object