* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Time (s)
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
One-way speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
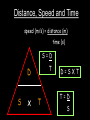
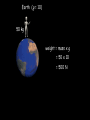
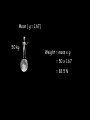
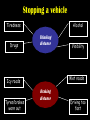
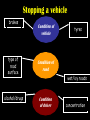
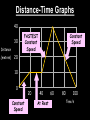
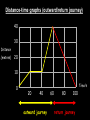
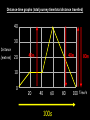
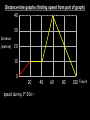
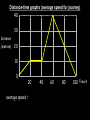
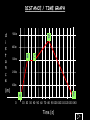
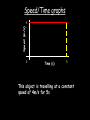
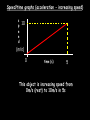
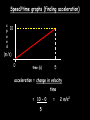
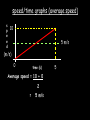
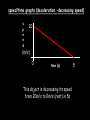
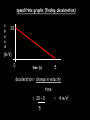
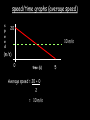
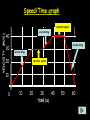
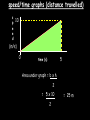
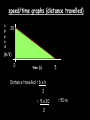
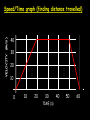
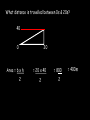
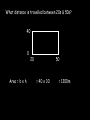
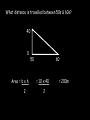
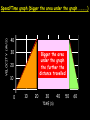
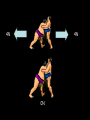
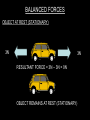
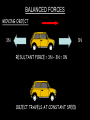
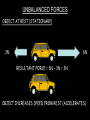
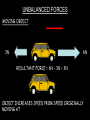
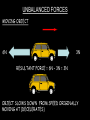
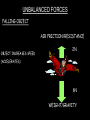
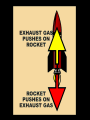
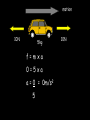
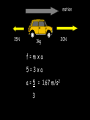
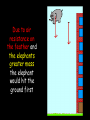
Distance, Speed and Time speed (m/s) = distance (m) time (s) S=D T D S x T D=SXT T=D S 1. An athlete runs 200m in 20s. What is his speed? speed = distance time speed = 200 m 20 s speed = 10 m/s 2. A bus travels 2000m between stops at a speed of 40m/s. Find the time taken to travel this distance. speed = distance time 40 = 2000 time time = 2000 = 50s 40 3. It takes a cyclist 30s to go 850 m. What is her speed? speed = distance time speed = 850 m 30 s speed = 28.33 m/s 4. A walker travels at 3m/s for a distance of 50m. How long did it take him? speed = distance time 3 = 50 time time = 50 3 = 16.67 s VELOCITY AND SPEED This car is travelling at a speed of 20m/s This car is travelling at a velocity of 20m/s east Distance and Displacement Distance is simply how far something has moved Man and dog have walked 3 metres from X x Displacement is ‘distance in a given direction’ Man and dog have walked 3 metres WEST from X x Acceleration acceleration (m/s2) = change in velocity (m/s) time taken (s) Remember: the formula for acceleration and deceleration is the same What does acceleration mean? The rate at which speed increases e.g. 5 m/s2 5m/s/s The speed is increasing by 5m/s every second 0s 1s 5m/s 2s 10m/s 3s 15m/s 4s 20m/s 5s 25m/s 6s 30m/s Questions on acceleration 1. A cyclist accelerated from rest to 10m/s in 5s. Find the acceleration. acceleration = change in velocity time = 10 – 0 5 = 2 m/s2 = 10 5 2. A sprinter crosses the finishing line at a speed of 8m/s and comes to rest 10s later. Calculate the deceleration of the sprinter. acceleration = change in velocity time = 8 – 0 = 8 10 = 0.8 m/s2 10 3. A grand prix car increases its speed from 50m/s to 120m/s in 3s. What is the acceleration? acceleration = change in velocity time = 120 – 50 = 70 3 = 23.33 m/s2 3 4. A skier increases his speed from 6m/s to 10m/s in 2s. What is his acceleration? acceleration = change in velocity time = 10 - 6 = 4 2 = 2 m/s2 2 MASS 15 kg 50 kg Mass is the amount of matter inside an object. It is measured in kilograms (kg) GRAVITATIONAL FIELD STRENGTH On Earth = 10N/kg g = 10 To find the WEIGHT of of an object you need to know the relationship between WEIGHT, MASS and GRAVITATIONAL FIELD STRENGTH weight (N) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg) = 1 x 10 = 10 N 1kg g = 10 10 N Weight is the force of gravity on a body and is measured in NEWTONS (N). On Earth the force on a 1kg object is 10N (g = 10N/kg). On the moon the force on a 1kg object is 1.67N (g = 1.67N/kg) What is the weight of the Martian if it lands on the Earth or the Moon? 50kg To find the weight of the Martian you need to know:weight (N) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg) W=MXG M=W G W G=W M G M Earth (g = 10) 50 kg weight = mass x g = 50 x 10 = 500 N Moon ( g = 1.67) 50 kg Weight = mass x g = 50 x 1.67 = 83.5 N STOPPING DISTANCE OF A VEHICLE Thinking distance Braking distance OVERALL STOPPING DISTANCE Stopping a vehicle Tiredness Drugs Alcohol Thinking distance Wet roads Icy roads Tyres/brakes worn out Visibility Braking distance Driving too fast Stopping a vehicle brakes type of road surface alcohol/drugs Condition of vehicle tyres Condition of road wet/icy roads Condition of driver concentration Distance-Time Graphs 40 30 Distance (metres) FASTEST Constant Speed Constant Speed 20 10 0 Constant Speed 20 40 At Rest 60 80 100 Time/s Distance-time graphs (outward/return journey) 40 30 Distance (metres) 20 10 0 Time/s 20 40 outward journey 60 80 100 return journey Distance-time graphs (total journey time/total distance travelled) 40 30 Distance (metres) 20 40m 40m 80m 10 0 20 40 60 100s 80 100 Time/s Distance-time graphs (finding speed from part of graph) Distance-time graphs (finding speed from part of graph) 40 30 Distance (metres) 20 10 0 20 40 60 80 speed during 1st 20s = distance = 10m = 0.5m/s time 20s 100 Time/s Distance-time graphs (average speed for journey) Distance-time graphs (average speed for journey) 40 30 Distance (metres) 20 10 0 20 average speed = 80m 100s 40 60 = 0.8 m/s 80 100 Time/s DISTANCE / TIME GRAPH d i s t a n c e (m) 500m D 400m B 300m C 200m 100m E A 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 110 120 130 140 Time (s) Questions on Distance/Time Graph Find: 1. the average speed during A-B S = D = 300m = 15m/s T 20s 2. the average speed between B – C S = D = 0m T = 0m/s 20s 3. the average speed for the return journey S = D = 460m = 7.67 m/s T 60s Speed/Time graphs Speed (m/s) 4 0 Time (s) 5 This object is travelling at a constant speed of 4m/s for 5s Speed/time graphs (acceleration - increasing speed) s 10 p e e d (m/s) 0 time (s) 5 This object is increasing speed from 0m/s (rest) to 10m/s in 5s Speed/time graphs (finding acceleration) s 10 p e e d (m/s) 0 time (s) 5 acceleration = change in velocity time = 10 – 0 5 = 2 m/s2 speed/time graphs (average speed) s p 10 e e d 5 m/s (m/s) 0 time (s) Average speed = 10 + 0 2 = 5 m/s 5 speed/time graphs (deceleration -decreasing speed) s p e e d 20 (m/s) 0 time (s) This object is decreasing its speed from 20m/s to 0m/s (rest) in 5s 5 speed/time graphs (finding deceleration) s p e e d 20 (m/s) 0 5 time (s) deceleration = change in velocity time = 20 – 0 5 = 4 m/s2 speed/time graphs (average speed) s p e e d 20 10 m/s (m/s) 0 time (s) Average speed = 20 + 0 2 = 10 m/s 5 Speed/Time graph VELOCITY (M/S) constant speed accelerating 40 30 decelerating accelerating 20 constant speed 10 0 10 20 30 TIME (S) 40 50 60 What is the acceleration in the 1st 20s? Acceleration = change in velocity time = 30 – 0 20 = 1.5m/s2 What is the deceleration in the last 10s? deceleration = change in velocity time = 40 – 0 10 = 4m/s2 Speed/Time graphs (finding distance travelled) Speed (m/s) 4 area of the green rectangle 0 Time (s) 5 distance = area under the graph distance = speed x time = height x length =4x5 = 20m speed/time graphs (distance travelled) s 10 p e e d (m/s) 0 5 time (s) Area under graph = b x h 2 = 5 x 10 2 = 25 m speed/time graphs (distance travelled) s p e e d 20 (m/s) 0 5 time (s) Distance travelled = b x h 2 = 5 x 20 2 = 50 m VELOCITY (M/S) Speed/Time graph (finding distance travelled) 40 30 20 10 0 10 20 30 TIME (S) 40 50 60 What distance is travelled between 0s & 20s? 40 0 20 Area = b x h 2 = 20 x 40 2 = 800 2 = 400m What distance is travelled between 20s & 50s? 40 0 Area = b x h 20 50 = 40 x 30 = 1200m What distance is travelled between 50s & 60s? 40 0 Area = b x h 2 50 60 = 10 x 40 2 = 200m VELOCITY (M/S) Speed/Time graph (bigger the area under the graph ………..) 40 30 Bigger the area under the graph the further the distance travelled 20 10 0 10 20 30 TIME (S) 40 50 60 RESULTANT FORCES When 2 or more forces act on an object they can be replaced by a single force called the RESULTANT FORCE 6N 6N 12N RESULTANT FORCES 4N 4N 0N RESULTANT FORCES 16N 29N 12N 1N BALANCED FORCES OBJECT AT REST (STATIONARY) 3N 3N RESULTANT FORCE = 3N – 3N = 0N OBJECT REMAINS AT REST (STATIONARY) BALANCED FORCES MOVING OBJECT 3N 3N RESULTANT FORCE = 3N – 3N = 0N OBJECT TRAVELS AT CONSTANT SPEED UNBALANCED FORCES OBJECT AT REST (STATIONARY) 3N 6N RESULTANT FORCE = 6N – 3N = 3N OBJECT INCREASES SPEED FROM REST (ACCELERATES) UNBALANCED FORCES MOVING OBJECT 3N 6N RESULTANT FORCE = 6N – 3N = 3N OBJECT INCREASES SPEED FROM SPEED ORIGINALLY MOVING AT UNBALANCED FORCES MOVING OBJECT 3N 6N RESULTANT FORCE = 6N – 3N = 3N OBJECT SLOWS DOWN FROM SPEED ORIGINALLY MOVING AT (DECELERATES) BALANCED FORCES FALLING OBJECT AIR FRICTION/RESISTANCE FALLS AT A CONSTANT SPEED (TERMINAL VELOCITY) WEIGHT/GRAVITY UNBALANCED FORCES FALLING OBJECT AIR FRICTION/RESISTANCE OBJECT INCREASES SPEED 2N (ACCELERATES) 6N WEIGHT/GRAVITY UNBALANCED FORCES FALLING OBJECT AIR FRICTION/RESISTANCE 8N OBJECT DECREASES SPEED (DECELERATES) REMEMBER: THE WEIGHT OF THE OBJECT REMAINS THE SAME NO MATTER WHAT SPEED IT FALLS AT 6N WEIGHT/GRAVITY AS SPEED INCREASES THE RESISTIVE FORCES INCREASE WEIGHT/ GRAVITY ALWAYS STAYS THE SAME UNBALANCED FORCES AIR FRICTION/RESISTANCE 20m/s 2N 6N 30m/s 5N 6N WEIGHT/GRAVITY ACTION/REACTION FORCES For every ACTION force there is an EQUAL but OPPOSITE REACTION force Wall pushing man Man pushing wall RECOIL BULLET REACTION FORCE ACTION FORCE What 2 things affect the acceleration of this car? • MASS measured in kilograms • RESULTANT FORCE, the difference between the force due to friction and the force of the engine Resultant Force, Mass and Acceleration resultant force (N) = mass (kg) x acceleration (m/s2) f= mxa F a=f m M A m=f a motion 10N 5kg 10N f=mxa 0=5xa a = 0 = 0m/s2 = constant speed 5 motion 15N 3kg f=mxa 5=3xa a = 5 = 1.67 m/s2 3 20N 55m/s2 300N f = m x a 300 = m x 55 m = 300 = 5.45 kg 55 ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY If an elephant and a feather were dropped from the same height, which one would hit the ground first? Due to air resistance on the feather and the elephants greater mass the elephant would hit the ground first If we ignore air resistance the elephant and feather would land on the ground at the same time due to their ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY being the same!!! All objects will accelerate downwards at the same rate if air friction is ignored so they will hit the ground at the same time! The acceleration g = 10m/s2