* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces and Motion
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
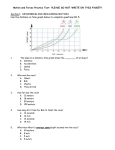
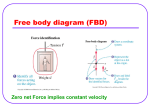
Forces and Motion Why do objects move? A force acts on them a FORCE is a push or a pull, in any direction,that may cause a change in an object’s motion Will a force always cause an object to move? NO Every object has several forces always acting on them. Gravity Air Pressure Friction Air Pressure Friction Normal The sum of all the forces acting on an object is called NET FORCE If an object is motionless, the Net Force = 0 , The forces are said to be Balanced. With Balanced Forces, the forces are equal but in opposite directions Since the applied force is not The forces are said to be stronger than the force of friction Balanced… the object does not move Gravity Air Pressure Applied Force Air Pressure Friction Normal If a force is exerted on an object causing it to move, this is called an UNBALANCED FORCE, the net force is greater than zero and the object moves. If the applied force is strong enough than to over The applied force is stronger come the existing forces, objectofwill friction… this is an the example an move Unbalanced force Gravity Air Pressure Air Pressure Friction Applied Force Normal Some Common Forces Friction The force exerted when two objects rub up against each other. Friction opposes motion, it causes objects to slow down What effects the Friction between objects? • Mass of the Object • Type of Surface • Amount of surface area touching Sliding Friction Motion Friction Rolling Friction The amount of friction between the two objects is less than sliding friction The object is easier to move Liquid Friction A lubricant, such as oil, makes a thin layer between the two objects. Which one will move farther if an equal force is applied 200 kg 1000 kg Which one will move farther if an equal force is applied On ICE 200 kg On Carpet 200 kg Which one will move farther if an equal force is applied 200 kg 200 kg Gravity • The force that pulls objects towards each other • Every object has gravity, meaning that all objects are being pulled toward each other. • So why are we not being pulled together right now? The larger the object is, the more we are effected by its gravitational pull. We are more attracted to the Earth’s gravity than we are to gravity of the things in the room Where will the red ball move Since the green ball is bigger, its gravity effects the red ball more than the white ball does, so the red ball moves towards the green ball Why do the two objects not hit the ground at the same time? Gravity is acting more on the elephant than on the feather. And a heavier object overcomes the upward force of wind resistance (friction) more easily thus falling faster than the light object What happens if we can eliminate the wind resistance? The two objects hit the ground at the same time Gravity is still acting more on the elephant than the feather, but the inertia of the elephant keeps it from accelerating faster All objects will accelerate the same when the force of gravity is the only force action on it. Motion When the position of an object is changing An object is in motion when the distance between two objects is changing How does a force effect the motion of an object? When a force is applied to an object it can change its motion by causing it to speed up, slow down or change directions How can we tell if an object is in motion? Use a Reference Point, A place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is moving Speed How fast an object is moving The distance an object travels in a certain unit of time Equation for Speed Speed = Distance __________ Time Speed Problem A person drives a car for 5 hours and goes 150 miles, how fast was he traveling? 150 miles Speed = _________ 5 hours = 30 miles per hour Velocity Speed in a certain direction Velocity Problem A person drives a car from Houston to Dallas it took 5 hours to go the 300 miles, What was his velocity Velocity = 300 miles _________ 5 hours = 60 mph NORTH Direction from Houston to Dallas Acceleration The rate at which velocity changes When does something accelerate It speeds up…. It slows down … Remember that velocity involves direction Changes direction… An object may be moving at a constant speed but if it changes direction it is said to be accelerating N W E S Say the speed of this ball is 10 mph. Its Velocity is 10 mph EAST. It has no speed in any other direction. N W E If the ball changes direction, it then has a velocity of 10mph in the new direction, which is south here. S Velocity = 10 mph East, and 0 mph South Change of direction = acceleration Velocity = 10 mph South, and 0 mph East VELOCITY = SPEED + DIRECTION • If you chance the speed, does the velocity change? Yes If you change the Direction does the Velocity change? Yes So if you change either the speed or direction Velocity changes Is it accelerating A ball rolling to a stop? YES… its slowing down or decelerating Is it accelerating A car traveling at 30 mph then going up to 60 mph to pass a slower moving car? Yes… it changed its speed from 30mph to 60mph The moon orbiting around the Earth YES! The moon may be at a constant speed, but it is constantly changing directions Graphing Speed What was the speed of the object at Point A B A Distance = 250 meters Time = 15 seconds Speed = distance/time 250meters/15 seconds= B 16.6 m/s A Distance = 250 meters Time = 15 seconds What was the speed of the object at Point B B A Distance = 500 meters Time = 30 seconds Speed = distance/time 500meters/30 seconds= B 16.6 m/s A Distance = 500 meters Time = 30 seconds A straight line means the object has a constant speed It is not speeding up or slowing down Object A Which object had the faster speed Object B Object A Object B 500m/30s = 16.6m/s 100m/30s = 3.3m/s The steeper the slope, the faster the object went Describe the object’s motion at point A D A C B It has stopped What is the speed of the object at Point B? A B D C O m/s, a flat line means the object has stopped What is the objects speed at point C? 5 seconds 50 Meters A B C 50m/5s = 10m/s D What is the Average Speed of the Object? Average speed = total distance/total time D A C B 350m/30s = 11.6m/s S = 16.6 m/s An upward curved line means that the object is accelerating, it keeps getting faster and faster S= 8.8 m/s S= 6.6 m/s How do we find Acceleration Final velocity – Initial Velocity/ time Final velocity – Initial Velocity/ time 16.6 m/s - 0 m/s / 30 s 16.6m/s / 30 s = .55m/s 2 A downward sloped line means the object is slowing down Sir Isaac Newton and the 3 Laws of Motion Inertia The resistance of an object to changes in motion Basically Stated… its harder to alter the motion of a heavier object than a lighter object Newton’s First Law An object in motion will stay in motion and an object at rest will stay at rest until acted on by a force. Basically stated… objects keep moving until something slows them down (friction) and objects will stay still until something causes them to move (force) Newton’s First Law Applied: As the wall stops the car… the guy keeps going, there is nothing to stop his forward motion Newton’s First Law Applied: as the truck stops, there is nothing keeping the ladder from stopping; it continues to move forward until gravity and wind resistance stops it Newton’s Second Law Shows the relationship between an objects mass its acceleration and the applied force. Basically stated… it takes a stronger force to move a heavier object that a lighter object and a stronger force to get an object to move faster Newton’s Second Law Applied: If an equal force is applied, the less massive object moves farther 200 kg 1000 kg Newton’s 2nd Law Applied: In order to move the more massive object the same distance at, it will take a much larger force 200 kg 1000 kg Newton’s Third Law For every action, there is an opposite and equal reaction Basically stated… apply a force in one direction, there is the same force being applied right back at you Action: Thrust Reaction: Jet moves forward As the swimmer pushes against the water, the water pushes back and the swimmer moves forward Which Law Applies If you step off a boat, the boat is moved backward THIRD LAW Which Law Applies Second Law; its harder to throw a heavy object than a light one Which Law Applies? Third Law: the downward force causes the space ship to go up Which Law Applies? nd 2 law: it takes a big force to mover the heavy object First Law: The object will not move until something causes it to move Would this cart be able to make the loop on this roller coaster? Newton’s 3rd law says every action has an equal reaction… Here is the action force… Remember.. Equal… not greater… So the reaction force can only be this high… Here is the action force… The cart would only go this high then fall back