* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PA2001: Energy and Momentum
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
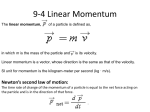
PA2001: Time and Energy Energy and Momentum Work and energy Power Potential energy Conservation of momentum Pressure in a fluid Tipler Chapters 6,7,8 and 13 Dr Mervyn Roy, S6 Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Work A force does work when it acts on an object moved through a distance. Motion in 1D with constant force: Work is a scalar quantity that is positive if Δx and F is the same sign, and negative if they are opposite – units are Joules = Newton metres Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Energy and work are related • When work is done by one system on another energy is transferred between the two systems. • Total energy is always conserved (read Tipler Chapter 7). Types of Energy • Kinetic energy – associated with the motion of an object. • Potential energy – associated with the configuration of a system. • Many types of potential and kinetic energy – e.g. Thermal energy. Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Work Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Work done by a variable force Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Work done by a variable force Work done = area under the graph of Fx against x Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Power Power is defined as the rate of doing work Units are Joules/second (or Watts) Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Power and acceleration At constant power, acceleration decreases with velocity e.g. Ford Fiesta max power = 50 hp mass = 1000 kg At 70 mph. Acceleration = Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Potential energy Potential energy is energy stored within a physical system. • exists when there is a force which tends to pull an object back towards its original position when it is moved. e.g. a stretched spring, or a weight suspended weight If the spring is released or the weight dropped, the stored energy will be converted back to kinetic energy and the restoring force will accelerate the object back towards its original position. Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Potential energy define e.g. spring Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Momentum is conserved Before collision Energy is conserved Energy and Momentum After collision PA2001: Time and Energy Examples Inelastic collision Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Examples Elastic collision Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Pressure in a Fluid P=F/A When a body is submerged in a fluid, the fluid exerts a force perpendicular to the surface of the body at each point on the surface. area, A Variation of pressure with depth Po h P Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Archimedes Principle Fs PoA Fs Fs Buoyant force equal to the weight of the displaced fluid B PA Energy and Momentum mg mg PA2001: Time and Energy F = mg - B Energy and Momentum PA2001: Time and Energy Examples Energy and Momentum