* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download scientific method
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek warfare wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Greek mythology wikipedia , lookup
Greek Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
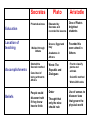
There was no single Greek religion. Officials in each polis were in charge of public feasts and sacrifices. Greek priests and priestesses often served as oracles, or persons who, it was believed, could speak with the gods. Oracles generally give advice in the form of a prophecy, or a statement of what might happen in the future. During the Golden Age, the Greeks worshiped the gods of Mount Olympus. There were 12 major gods and goddesses. Each had specific duties to carry out. The Greeks placed importance on the worth of the individual, allowing them to approach their gods with dignity. The Greeks built temples and held festivals, including the Olympic Games and the theater, to honor their gods. Mount Olympus and the Gods of Greek Religion Every four years, in the middle of summer, a festival was held in Olympia to honor the god Zeus. The festival was known as the Olympic Games and was the most important sporting event in Greece. Athletes came from all over Greece and from Greek colonies in Africa, Italy, and Asia Minor to take part in the games. Only men were allowed to take part; women were not even allowed to watch. The Olympics were made up of many events including: chariot races, Boxing, pancratium–a combination of boxing and wrestling, pentathlon–made up of five events: running, jumping, throwing the discus, wrestling, and hurling the javelin Between the different events at the games, poets read their works aloud. Herodotus, the “Father of History,” first read his account of the Persian Wars at the Olympics. The theater grew out of festivals given in honor of the god Dionysus. About the time of the Persian Wars, a Greek poet named Aeschylus added an additional character to each story. He created what came to be known as a play. The first Greek plays were tragedies, or stories about suffering. All dealt with the past and with the relationships between people and gods. Three of the great writers of tragedy were Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides. The comedy, or a play with a happy ending, came into being soon after. Greek comedies were about the present. One of the greatest writers of Greek comedy was Aristophanes. Greek plays were performed only at community festivals in open air theaters. Each actor wore a huge canvas and plaster mask that showed the sex, age, and mood of the character. The Greeks believed support of the theater was a public responsibility. The Olympic Games Among the things on which the Greeks placed great importance was intellect, or the ability to learn and reason. To the Greeks, studying the laws of nature and loving wisdom were the same thing; they called it philosophia. Today, people who search for such knowledge and wisdom are known as scientists and philosophers. Much of what they know is based on the thoughts of the Greeks. In 399 B.C., Socrates, a 70-year-old Athenian philosopher, was tried in Athens. He believed people could discover truth if they knew how to think. In his search for truth, Socrates walked throughout Athens trying to teach people how to think. He did this by asking questions. This form of questioning is known as the Socratic method. Socrates was tried before a jury of some 500 citizens and sentenced to death. All that is known about Socrates comes from one of his pupils, an Athenian aristocrat named Plato. Plato set up the Academy, a school to train government leaders, outside Athens in the sacred grove of the hero Academus. He thought political liberty was disorder and did not approve of it. Plato set down his ideas about an ideal state in a book called The Republic –the first book ever written on political science. In a work called The Dialogues, Plato showed how difficult it is to discover truth. They consist of a series of discussions in which different people talk about such things as truth and loyalty. Aristotle was one of Plato’s brightest pupils. Before he died in 322 B.C., he founded his own school in Athens and wrote more than 200 books. He believed in using one’s senses to discover the laws that govern the physical world. Aristotle also added to the ideas of an early Greek scientist named Thales of Miletus. Thales developed the first two steps of what is known today as the scientific method. First, Thales collected information. Then, based on what he observed, he formed a hypothesis, or possible explanation. Aristotle said that a hypothesis must be tested to see if it is correct. Aristotle contributed the syllogism ,a method of reasoning that uses three related statements to logic, or the science of reasoning Socrates Plato Private business Education Educated by Socrates and recorded his lessons Location of teaching Greece, Egypt and Italy Accomplishments Walked through Athens Started the Socratic method Convicted of being a threat to Athens Beliefs People could discover truth if they knew how to think Academus in Athens Wrote The Republic and Dialogues Aristotle One of Plato’s brightest students Founded his own school in Athens First to classify plants and animals Scientific method Wrote 200 books Order Thought that only the wise should rule Use of senses to discover laws that govern the physical world ANCIENT GREEK PHILOSOPHY that natural events way gods behave. Greek scientistsGreek Scientists.ppt discovered are not caused by the They also learned that the world is governed by natural laws that people can discover and understand. Thales of Miletus not only developed the first two steps of the scientific method, but also correctly predicted an eclipse of the sun in 585 B.C. The “Father of Scientific Medicine” was Hippocrates. Hippocrates drew up a list of rules about how doctors should use their skills to help their patients, which is known today as the Hippocratic Oath. Doctors all over the world still promise to HEALING in Ancient Greece How important was religion in ancient Greek civilization? How did tragedies differ from comedies? Why is the scientific method important to modern science? What would you have done if it had been your decision whether or not to put Socrates on trial?