* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Routing Overview
Global serializability wikipedia , lookup
Commitment ordering wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
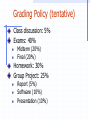
CS461: Principles and Internals of Database Systems Instructor: Ying Cai Department of Computer Science Iowa State University [email protected] Office: Atanasoff 201 Office Hours: MT 2:00pm-3:00pm Database A collection of related data [Elmasri] A database represents some aspect of real world called “miniworld” [Elmasri] or “enterprise” [Ramakrishnan] A database can be of any size and of varying complexity. It may be generated and maintained manually or using computers Database Management System (DBMS) A software package designed to store and manage databases Relational DBMSs: DB2, Informix, Oracle, Microsoft Access, Microsoft SQL Server, FoxBase, Paradox Objectives To understand database design techniques and theories behind design/implementation of some components of database management system (DBMS) Some advanced topics To be familiar with some commercial relational database management systems To experience working as a team, consisting of 3-4 members Course Materials Reading materials Database Management Systems (3rd ed.), by R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke. Others will be posted on the Internet Lecture notes available for downloading on the course web site http://www.cs.iastate.edu/~cs461 Topic Coverage Part 1: Database design Introduction, conceptual database design (chapters 1-3) Review of SQL (Chapter 5) Schema refinement and normal forms (Chapters 19-20) Database application design and development (through project) Topic Coverage Part 2: Database Internals Relational Algebra (Chapter 4) Storage and Indexing (Chapters 8-9, 10.1, 10.3-10.6) Query evaluation (Chapters 12-14) Query optimization (Chapter 15) Transaction management (Chapters 16-17) Topic Coverage Part 3: Advanced Topics Security Spatial indexing Mobile object database management Data mining Internet search Team Project What to do Your idea Project manager Main contact with the instructor Task and time allocation Lead efforts in requirement analysis, project report and presentation DBA Lead database design, implementation, and database security Lead developer Code development and review Grading Policy (tentative) Class discussion: 5% Exams: 40% Midterm (20%) Final (20%) Homework: 30% Group Project: 25% Report (5%) Software (10%) Presentation (10%) Mutual Contract Instructor I will provide information about database principles and practice to the best of my knowledge I will uphold my professional ethics Students I will participate in this course and practice concepts learned through lectures, assignments, exams, and team projects to the best of my ability I will uphold academic honesty, professional ethics and be a good class and world citizen Other Policies Academic Honesty Students who plagiarize other work in any part of assignment/tests will receive F as the letter grade for this course, and will be reported to the university. Disability If you have a documented disability and anticipate needing accommodations in this course, please make arrangements to meet with me soon.