* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 2: Structure a Database
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
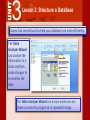
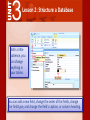
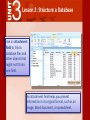
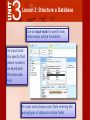
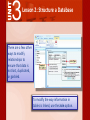
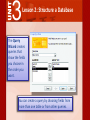
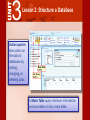
3 Access 2007® Use Databases How can Microsoft Access 2007 help you structure your database? 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Access features such as templates, tables, and queries can help you to structure your database, making it easier to find and interpret data. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Lesson 2 Objectives: Use database templates and create blank databases Create tables and change their structure Create relationships between tables Create different types of queries 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database To create a database, you can search both Access and online to find the appropriate template. Database templates include tables and fields for organizing and tracking data, such as inventory, customer orders, personal contact information, and todo lists. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database If you cannot find a template to meet your needs, you can create one from blank database. You can then design your own tables, forms, and reports. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database You can add new tables to any database. To create a table, select a template from the dozens Access provides for business and personal use. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Use Design View to design your own tables. In a table, you can change a field’s property, such as the number of characters, or change a field data type, such as whether it represents a date/time. Every table must have a primary key. A primary key ensures that each record is unique. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Access has several tools to help your database run more efficiently. The Table Analyzer Wizard can analyze the information in a table and then make changes to streamline the data. The Table Analyzer Wizard can ensure addresses are listed consistently and get rid of repeated listings. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database With a little patience, you can change anything in your tables. You can add a new field, change the order of the fields, change the field type, and change the field’s caption, or column heading. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database The Totals row function offers a quick and simple way to summarize columns of data in a table to get totals, averages, maximums, minimums, and other calculations. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Access allows you to set properties for entire tables of data and for individual fields. The field properties are shown as a list in a Property Sheet. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Use multivalued fields to store more than one answer in a single field. A sporting goods store might categorize knee pads in both the skateboarding and baseball categories. You can create a Lookup field, which will contain all the possible data choices for the field. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Use an attachment field to link to database files and other objects that might not fit into one field. An attachment field helps you present information in its original format, such as an image, Word document, or spreadsheet. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Use an input mask to specify how information will be formatted. An input mask can specify that phone numbers be keyed with the area code first. An input masks keeps users from entering the wrong types of data into certain fields. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Access is a relational database because it lets you define relationships as part of the database structure. A relationship is a link between two tables based on a common field. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database A one-to-one relationship means that both fields in their respective tables are not repeated. Table 1 Table 2 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database A one-to-many relationship means that a record in one table can have many matching rows in another table. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Referential integrity makes sure that the related data in two tables always exists and is complete. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database There are a few other ways to modify relationships to ensure that data is not lost, duplicated, or garbled. To modify the way information in tables is linked, use the Join option. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database The Query Wizard creates queries that show the fields you choose in the order you want. You can create a query by choosing fields from more than one table or from other queries. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database The Query Wizard includes several preset queries to help you analyze and manage your data. An unmatched query finds records without a matching related date. A duplicate query finds multiple records that contain the same data in a field. A crosstab query shows summary data (such as count, average, or sum) grouped by two fields. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Action queries take action on the data in databases by adding, changing, or deleting data. A Make Table query retrieves information and assembles it into a new table. 3 Lesson 2: Structure a Database Other types of action queries include the Update Query, which updates information in a table, the Delete Query, used to delete records, and the Append Query, which inserts new records.