* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CCLRC Template - National e
Semantic Web wikipedia , lookup
Data Protection Act, 2012 wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
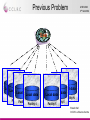
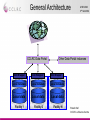
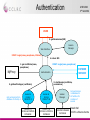
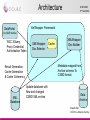
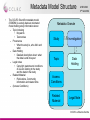
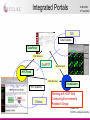
The CCLRC DataPortal Shoaib Sufi AMH 2004 Nottingham CCLRC e-Science Centre Background • Motivation – – – • A interactive data access gateway to scientific data. Making existing scientific data resources accessible through a single interface. Acting as a broker between scientists, facilities and data. Why is it needed? – – – • Grid enable facilities at CCLRC Many instruments and experiments run; on Synchrotron , Neutron Spallation, Lasers Make data accessible, support single sign on integration, facilitate 3rd party transfer, allow machine access for composition of data into workflow systems What is the Data Portal? – – – • AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 Currently scientists have limited support for accessing, managing and transferring data. The Grid hopes to provide computational and analytical services. The scientist need some why of finding and transferring the data for these ‘grid services’. Benefits – – – – Repetition of experiments can be avoided. Collaborations can be built by identifying that someone else is working in a similar area. Data about a related material can be found and used to aid a new analysis. Data can be rediscovered and reanalysed when better analysis tools becomes Shoaib Sufi available CCLRC e-Science Centre Current Uses AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • Generic Data Portal – Allows data access for 4 facilities: • The Synchrotron Radiation Department. • The Neutron Spallation Source. • The British Atmospheric Data Centre (NERC Data Center). • Max-Planck Institute for Meteorology. • e-Minerals Mini-Grid – Environment from the molecular level. – Environmental problems, such as transport of pollutants, weathering, and containment of high-level radioactive waste require a understanding of the processes at a molecular level. – Computer simulations at a molecular level can give considerable progress in our understanding of these processes. • e-Materials – Combinatorial materials science and polymorph prediction. – Again, simulations can progress their understanding. Integrative Biology – Used as part of the data management infrastructure • Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Previous Problem AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 User Local data Local Local data data Local data Facility 1 FacilityFacility 1 1 Local data Local data Local data Facility N Facility 4 Facility 6 Facility 5 Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre General Architecture CCLRC Data Portal AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 Other Data Portal instances Xml Wrapper Xml Wrapper Xml Wrapper Local metadata Local metadata Local metadata Local data Local data Local data Facility 1 Facility 2 Facility N Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Core Modules AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • Web Interface, Query and Reply, Lookup and Help. • Important function grouped into modules, each modules with a web service interface, interface description in WSDL and communicate via SOAP. Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Additional Modules AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • Access Control, Authentication and Authorisation, Data Transfer, Shopping Cart, User Administration, Facility Administration and Accounting. • Functions grouped into modules, each with web services interface. These Modules could be user by others or exchanged with ones that have the same interface but better Shoaib Sufi implementation. CCLRC e-Science Centre External Services AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • XMLWrappers, HPC Portal, Visualisation Portal, SRB, other DataPortal Instances . • Other services that are linked with the DataPortal, but are not integral part of it. Registered with the Portal and accessible via web services interface. Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Authentication AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 USER 5: getPermissions(SID) Session Manager Web Interface START: Login(name, passphrase, lifetime) 4: return SID 1: get certificate(name, passphrase) MyProxy START: Login(name, passphrase) 3: startSession(certificate, permissions) 2: getUserPrivileges (certificate) Get permissions from database for facility A OUTSIDE SERVICE Authentication Access & Control FACILITY A Access & Control FACILITY B FACILITY A ACCESS & CONTROL DATABASE FACILITY A ACCESS & CONTROL DATABASE Session Manager SESSION MANAGER DATABASE Set permissions in database for all facilities for duration of session Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Authorisation Data Portal AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 Facility 1) Delegated Globus credential Access And Control 2) Access and Control maps user’s DN to local facility’s system and obtains user’s access rights to facility. Data Portal Authentication 3) Access and Control returns authorisation token 3) Access and Control creates an Authorisation Token and puts the access rights information into the Token. Then signs the Token with its private key. Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre XML Wrapper AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • Data archives hold metadata in different formats and format structures: – Databases (relational, object based) – Flat Files – XML • Needed by CCLRC Data Portal to convert from Data Archive format to XML implementation of the CCLRC Scientific Metadata Model (CSMDM) understood by the Data Portal • Act as an Adaptor layer giving the Data Portal a uniform view of differing metadata sources • API is what matters, but interesting to look at their architecture; good Wrappers support a full flexible and efficient applications built on top of them (e.g. CCLRC Shoaib Sufi Data Portal) CCLRC e-Science Centre Architecture AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 XmlWrapper Framework DataPortal (via Q&R module) W3C XQuery, Proxy Credential, Authorisation Token XMLWrapper: Doc Selector Metadata mapped from Archive schema To CSMD format Result Generation, Cache Generation & Cache Coherency XML Database Cache XMLWrapper: Doc Builder Update database with New and changed CSMD XML entries Data Archive Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Architecture • • AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 XML Wrapper Selection – The DataPortal supplies an • XQuery selector which is run against the archives metadata set (can also contain formatting directives) • Proxy Certificate – to check that the user is authentic • Authorisation Token – to check that the user has the right permissions to see the metadata – Security steps • Authorisation Token is checked to see that it has the same DN as the one in the Proxy certificate • Authorisation Token is checked to see if it was signed by the correct Authorisation Authority • Authorisation Token is checked to see the user is authorised to see the metadata. – Selection steps (if Security steps passed) • The XQuery is checked to see if the results already exist in the query cache • (if not) The XQuery is run against the XML stored in the XML-DB • The Results are returned using (web services) XML Building – The Document Builder converts all studies in the Archive into CSMD records and inserts them into the repository – The Builder periodically checks for new studies or changes to existing studies and updates the repository Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Benefits • • • • • AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 No need to support a custom API – The use of XQuery allows XML Wrapper users to extract the information they need once the CCLRC Scientific Metadata XML Schema (CSMD-xml) is known by the user of the wrapper. Queries work on the XML-DB CSMD representation of the archive in one go; however due to efficient indexing of nodes by such XML-DB’s such as eXist the computational cost is not prohibitive Does away with (or lessens) the need for XSLT scripts on the Data Portal as XQuery can do all (or the majority) of the formatting work. Architecture is De-coupled from XML Schema – this architecture could equally be used to serve other XML Schema formats (just need a new XMLWrapper DocBuilder) There is a need to be aware of cache coherency issues – XML-DB cache – XML Selector cache – Use timestamps to update whole records when one item changes in a particular study (CSMD) record – this is the preferred solution at the moment Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Metadata Model Structure • The CCLRC Scientific metadata model (CSMDM) is a study-data set orientated model holding study information about: – Topic Indexing • Keywords • Taxonomies – Provenance • What the study is, who did it and when – Data Holding • Detailed description about what the data is and its layout – Legal notes • Copyright, patents and conditions of use etc relating to the study and the data in the study – Related Material • Publications, Community information and related links – (Access Conditions) AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 Metadata Granule Study 1 M Investigation 1 1 Topic Data Holding Access Conditions Related Material Legal Note Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Features AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • Allows for indexing by keywords & topics and increasing levels granularity: – Study, Investigation Data Set, Data Object • Can also hold parameter information for data object and data sets • Has Conformance Levels – Increasing amounts of metadata and indexing • Enumerations: controlled vocabularies suggested for static data e.g. – Classification systems for Topic Indexing – Standard Parameter names/units Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre HPC Portal AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • Another e-Science Centre project to develop a Web portal to search for resources and submit HPC applications to a computational Grid. • Uses Globus toolkit v2.2 • Functionalities include: – Resource Management: GRAM. – Information Services: MDS. – Data Management: GridFTP and GASS. – All use GSI security protocol as the connection layer. Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Integrated Portals AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 GSI Data Systems DataPortal Web Services GridFTP Web Services HPCPortal Web Services Visualisation HPC Systems Globus Working with GGF Grid Computing Environments Research Group Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Single Sign on AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • How do you have single sign on? • Both HPC and DataPortal have their own Session Managers which rely on Globus Proxy Credentials. • Integrated session managers communicate over SSL using mutual authentication between the web servers. • Allows user’s credentials to be delegated between portals allowing single sign on. • The certificate can then be used for GSI authentication. Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Single Sign on AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 USER START: Log on to DataPortal then to HPC Portal FINISH: User is sent to HPC front page to use its services 3: LoginHPC(SID) DataPortal HPC Portal 8: HPC Session id 1: Login(username, password,lifetime) Via Authentication Module Dataportal Session Manager 2: Dataportal SID 7: TRUE 6: Delegated Credential 4: isValid(SID) HPC Session Manager 5: RequestCert(SID) Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Scenario AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 • User logs on to Data Portal and searches for data. • The data found and link to the are added to the persistent shopping cart. • The user could then transfer the data to another machine using GSI FTP, either using the Data Portal or the HPC Portal. • Using single sign on, the user could then go directly to the HPC, run a remote job run on the data they have just transferred (using e.g. GSI FTP) and then transfer the results back to their machine for analysis. Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre Questions AHM 2004 3rd Set 2004 ? Shoaib Sufi CCLRC e-Science Centre