* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spreadsheet vs Database
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
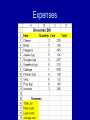
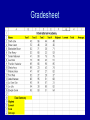
Spreadsheet vs Database • When do we use them? Spreadsheet review • Why do we use a spreadsheet? Spreadsheet review • Enter data • Do calculations on data • Examples: expenses, profit/loss Expenses Gradesheet Database • Store information long-term • Search information An example… • What sort of information does Ren Da Fu Zhong need to keep? • Think of at least 10 pieces of information! RDFZ stores information on… • Students: – Name, address, ID number, parents, grades, classes, teachers, payment info, absences, extra activities • Teachers: – Name, address, ID number, classes taught, students taught, grades given, bank information, payment information RDFZ stores information on… • Other employees: – Name, job, hours worked/week, pay scale, bank information, duties/responsibilities • Inventories: – How many classrooms, how many desks, chairs, overhead projectors, scanners, computers… RDFZ stores information on… • Lots of stuff! • Can all of this fit on one spreadsheet? – No! – This is when we use a database. Uses of a database • • • • • Store data Backup data Add/Modify data Query data (ask questions) Generate reports (print data in an easy-toread format) Examples of databases • Can you think of any? Your music Your games Your web pages Your life Warning! • Databases are very different from word processors, spreadsheets, or presentation software. • You CANNOT just start typing. • A database must be DESIGNED before you start adding data. • Why? Why? • Avoid duplication (putting in the same data many times) • Logical organization of data The parts of a database • Do you remember: – Columns? – Rows? – Cells? • These have different names in a database… Table: one page Column = Field • We have 3 fields: ID, title, and date • Notice – every field has the same data type! • This is required! Data Type review • Remember these from Excel? Row = Record • Here we have 4 records • Each record has all the information from one entry. Another example • Here we have 3 records • A record has all the info on one entry Cell: Data Value • How many data values are in this table? Primary Key • Here, the “Video Collection” field is the primary key • EVERY table MUST have a primary key – a unique value Primary Key Examples Designing a Database • Before we enter data, we must design the table • Things to think about: – What fields do we need? – What data type does each field need? – Which field can become the primary key? Example: RDFZ • What information will RDFZ store about students? • What data type should each be? • Which field will make a good primary key? Example: Taobao business • We are running a business on TaoBao. We are selling clothing on the internet. We want to make a database of all the orders that we receive. • What information must we store? • What data type should each field be? • What should be the primary key? Example: a new home • We are real estate agents, and need to build a database of all apartments in the area. • What information must we store? • What data type should each field be? • What should be the primary key?