* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Database
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
ContactPoint wikipedia , lookup
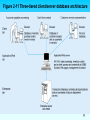
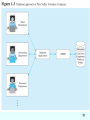
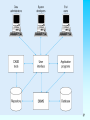
IS 4420 Database Fundamentals Leon Chen Agenda About yourself Name Major About the instructor Syllabus Chapter 1 2 IS 4420 Database Fundamentals Chapter 1: The Database Environment Leon Chen Overview Database environment and Client/Server architecture Database, data, information, and metadata Evolution of database systems Advantages of databases Costs and risks of databases Categories of databases Components of database environment 4 Figure 1-11 Components of the database environment Metadata Data 5 Figure 2-11 Three-tiered client/server database architecture 6 Definitions Database - organized collection of logically related data Data - stored representations of meaningful objects and events Structured: numbers, text, dates Unstructured: images, video, documents Information: data processed to increase knowledge of the user Metadata: data that describes the properties and context of user data (data about data) 7 Figure 1-1a Converting data to information - data in context 8 Graphical displays turn data into useful information that managers can use for decision making and interpretation 9 Metadata Data that describes the properties and context of user data (data about data) 10 Evolution of Database Systems Flat files (not database) - 1960s - 1980s Hierarchical – 1970s - 1990s Network – 1970s - 1990s Relational – 1980s - present Object-oriented – 1990s - present Object-relational – 1990s - present Data warehousing – 1980s - present Web-enabled – 1990s - present 11 DATABASE Approach Central repository of shared data Stored in a standardized, convenient form Requires a Database Management System (DBMS) A software system that is used to create, maintain, and provide controlled access to user databases 12 13 14 15 16 Figure 1-11 Components of the database environment 17 Components of the Database Environment CASE Tools – computer-aided software engineering Repository – centralized storehouse of metadata Database Management System (DBMS) – software for managing the database Database – storehouse of the data Application Programs – software using the data User Interface – text and graphical displays to users Data Administrators – personnel responsible for maintaining the database System Developers – personnel responsible for designing databases and software End Users – people who use the applications and databases 18 Match terms and definitions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Data Database application Repository Metadata Information DBMS Database ERP Enterprise data model a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. Data placed in context or summarized Application program Facts, text, graphics, etc. A graphical model about an organization Organized collection of related data Data definitions and constraints Centralized storehouse for all data definitions An integrated enterprise level MIS A software application to create, maintain and control a database 19