* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body System Graphic Organizer
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
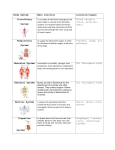
Body Systems Graphic Organizer Body System Respiratory System Function To supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. Organs The nose, throat, lungs, and passageways that lead to the lungs make up the respiratory system Breathing is made possible by your respiratory system. The respiratory system is the group of organs that take in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide Circulatory System (Cardiovascula r) Your heart creates pressure when it beats. This pressure moves blood throughout your body. To circulate all vital fluids throughout the entire body to nourish all of the body's systems; to transport blood, hormones, white blood cells and chemicals through the heart, lungs and all major organs. Your heart, blood, and blood vessels make up your cardiovascular system to break down the food we eat into smaller parts so the body can use them to build and nourish cells and provide energy Your digestive system is a group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used by the body. The liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and salivary glands are also part of the digestive system. But food does not pass through these organs. The human digestive tract can be more than 9 m long! The digestive tract includes your mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Urethra Digestive System Excretory System Your urinary system removes waste from blood and regulates your body’s fluids. Excretion is the process of removing waste products from the body. Three of your body systems have a role in excretion. Your integumentary system releases waste products and water when you sweat. Your respiratory system releases carbon dioxide and water when you exhale. Finally, the urinary system contains the organs that remove waste products from your blood. The kidneys are a pair of organs that constantly clean the blood. Your kidneys filter about 2,000 L of blood each day. Your body holds only 5.6 L of blood, so your blood cycles through your kidneys about 350 times per day! Nervous System Immune System Your nervous system receives and sends electrical messages throughout your body. The nervous system acts as the body’s central command post. It has two basic functions. First, it gathers and interprets information. This information comes from inside your body and from the world outside your body. Then, the nervous system responds to that information as needed. Brain Spinal cord (specialized structures; nerves) Also known as the lymphatic system. Returns leaked fluids to blood vessels and helps get rid of bacteria and viruses. The increased blood flow also brings cells that belong to the immune system, the body system that fights pathogens. The immune system is not localized in any one place in your body. It is not controlled by any one organ, such as the brain. Instead, it is a team of individual cells, tissues, and organs that work together to keep you safe from invading pathogens. team of individual cells, tissues, and organs Body System Skeletal System Function Muscular System Your bones provide a frame to support and protect your body parts. Bones, cartilage, and the connective tissue that holds bones together make up your skeletal system. Bones also help your body maintain homeostasis by storing minerals and making blood cells Works with the skeletal system to help your body move When you want to move, signals travel from your brain to your skeletal muscle cells. The muscle cells then contract, or get shorter. Organs Average adult has 206 bones. All throughout your body Integumentary System (skin) Endocrine System Protects the tissue that lies Skin beneath your hair, skin and nails Skin protects you by keeping water in your body and foreign particles out of your body. Skin keeps you in touch with the outside world. Nerve endings in your skin let you feel things around you. Skin helps regulate your body temperature. Small organs in the skin called sweat glands make sweat. Sweat is a salty liquid that flows to the surface of the skin. As sweat evaporates, the skin cools. Skin helps get rid of wastes. Several kinds of waste chemicals can be removed in sweat. Skin comes in many colors. Skin color is determined by a chemical called melanin. If a lot of melanin is present, skin is very dark. If little melanin is present, skin is very light. Melanin absorbs ultraviolet light from the sun. So, melanin reduces damage that can lead to skin cancer. Your glands send out chemical messages throughout your body The endocrine system controls body functions by using chemicals that are made by the endocrine glands. A gland is a group of cells that make special chemicals for your body. Chemical messengers made by the endocrine glands are called Multiple organs hormones. A hormone is a chemical messenger made in one cell or tissue that causes a change in another cell or tissue in another part of the body. Hormones flow through the bloodstream to all parts of the body. Reproductive System Male reproductive system: produces and delivers Female reproductive system: produces eggs and nourishes and protects the fetus • • Ovaries- female Testes- male