* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MANAGING DATA RESOURCES
Expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) wikipedia , lookup
Data Protection Act, 2012 wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Open data in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
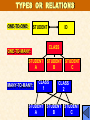
FILE ORGANIZATION • BIT: Binary Digit (0,1;Y,N;On, Off) • BYTE: Combination of BITS which represent a CHARACTER • FIELD: Collection of BYTES which represent a Fact • RECORD: Collection of FIELDS which reflect a TRANSACTION • FILE: A Collection of Similar RECORDS Managing Digital Data The layout of a personnel file in traditional file organization. FILE ORGANIZATION • DATABASE: An Organization’s Electronic Library of FILES • Primary FIELD or Key: Field in Each Record Uniquely Identifies THIS Record For RETRIEVAL UPDATING SORTING TRADITIONAL FILE ENVIRONMENT (FLAT FILE) • • • • • DATA REDUNDANCY PROGRAM / DATA DEPENDENCY LACK OF FLEXIBILITY POOR SECURITY LACK OF DATA SHARING & AVAILABILITY Different information making up a student record retained in three different sites. DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (DBMS) SOFTWARE TO CREATE & MAINTAIN DATA *** ENABLES BUSINESS APPLICATIONS TO EXTRACT DATA *** INDEPENDENT OF SPECIFIC COMPUTER PROGRAMS DBMS Managing Digital Data • Traditional Files vs. Databases: Pros and Cons – Traditional File Advantages • Simplicity • Efficiency • Customization – Database Advantages • • • • Reduced data redundancy Application/data independence Better control Flexibility COMPONENTS OF DBMS: • THE SCHEMA: describe the structure of the Database. DATA DEFINITION LANGUAGE: • Defines Data Elements in Database • and Used to construct the schema DATA MANIPULATION LANGUAGE: • Manipulates Data for Applications • DATA DICTIONARY: – Maintains all information supplied by the developer when constructing the schema * DBMS • Data Definition Language (DDL) Data definition language to create a schema in NOMAD Components of Database Management Systems • Data Manipulation Language (DML) – Used to query the database Figure 8.14 A Paradox query by example DATA DICTIONARY A typical data dictionary for a staff file ADVANTAGES OF DBMS: • REDUCES COMPLEXITY • REDUCES DATA REDUNDANCY • CENTRAL CONTROL OF DATA DEFINITIONS • REDUCES PROGRAM / DATA DEPENDENCE • REDUCES DEVELOPMENT / MAINTENANCE COSTS • ENHANCES SYSTEM FLEXIBILITY • INCREASES ACCESS / AVAILABILITY OF INFORMATION * DBMS Database Models HIERARCHICAL DATA MODEL – Records are related hierarchically – each category is a subcategory of the next level up – Disadvantages of hierarchical databases • To retrieve a record, a user must start at the root and navigate the hierarchy. • If a link is broken, the entire branch is lost. • Requires considerable data redundancy ROOT FIRST CHILD 2nd CHILD Employer Compensation Ratings Salary Job Assignments Pension Benefits Insurance Health NETWORK DATA MODEL • VARIATION OF HIERARCHICAL MODEL • Allows a record to be linked to more than one parent • USEFUL FOR MANY-TO-MANY RELATIONSHIPS NETWORK 1 NETWORK A NETWORK 2 NETWORK B NETWORK C RELATIONAL DATA MODEL • Consists of tables; links among entities are maintained with foreign keys • DATA IN TABLE FORMAT – RELATION: TABLE – TUPLE: ROW (RECORD) IN TABLE – FIELD: COLUMN (ATTRIBUTE) IN TABLE HOURS * RATE ABLE $ 40.50 $ 10.35 BAXTER $ 38.00 $ 8.75 CHEN $ 42.70 $ 9.25 DENVER $ 35.90 $ 9.50 TOTAL $ 419.18 $ 332.50 $ 394.98 $ 341.05 TYPES OR RELATIONS ONE-TO-ONE: STUDENT CLASS ONE-TO-MANY: STUDENT A MANY-TO-MANY: ID STUDENT B CLASS 1 STUDENT C CLASS 2 STUDENT STUDENT A B STUDENT C Relational Operations • Data Manipulation – Select : is the selection of records that meets certain condition. – Project: is the selection of certain columns from a table. – Join : is the joining of data from multiple tables. • Structured Query Language (SQL) – International standard DDL and DML for relational DBMS. – Advantages of using SQL Users do not need to learn different DDLs and DMLs. SQL can be embedded in widely used 3rd generation languages, increasing efficiency and effectiveness. Programmer not forced to rewrite statements since SQL statements are portable. Database Models Advantages and disadvantages of database models Database Architecture • Shared Resource and Client/Server Systems – Four basic client/server models • Applications run at a server • Applications run on local PCs • Applications run on both the local PCs and the server • Applications and key elements of the database are split between the PCs and the server Database Architecture • Distributed Databases – Replication :Full copy of the entire database is stored at all sites A replicated database: each computer holds a copy of the entire database Database Architecture – Fragmentation: Parts of database are stored where they are most often accessed A fragmented database: each computer holds only the part of the database that is most frequently accessed by the local users Web Databases • Databases on the Web – – – – Catalogs Libraries Directories Client lists and profiles • When linking a database to the Internet, consider • Which application to use • How to ensure Web surfers do not interfere with database updates • How to maintain security Data Warehousing • Data warehouse – Collection of data that supports management decision making – Phases in Building a Data Warehouse • Extraction Phase • Cleansing Phase • Loading Phase • Data Mining – Selecting, exploring, and modeling data to discover unknown relationships OPERATIONAL, HISTORICAL DATA Data Warehousing INTERNAL DATA SOURCES DATA WAREHOUSE DATA ACCESS & ANALYSIS EXTRACT, TRANSFORM INFORMATION DIRECTORY EXTERNAL DATA SOURCES QUERIES & REPORTS OLAP DATA MINING Data-Mining Potential applications of data-mining DATABASE ADMINISTRATION • DEFINES & ORGANIZES DATABASE STRUCTURE AND CONTENT • DEVELOPS SECURITY PROCEDURES • DEVELOPS DATABASE DOCUMENTATION • MAINTAINS DBMS * Ethical and Societal Issues A Too-Risky Info Highway • Out of Hand -- Out of Control – DBMSs allow organizations to collect, maintain, and sell vast amounts of private personal data easily. • Where is the Information Going? – Many consumers provide information daily without being aware of where it is actually going. – http://www.publicrecordfinder.com/ • The Upside – Database technology enables better and faster services.