* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meiosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
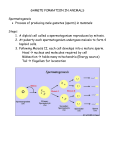
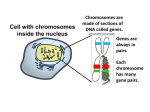
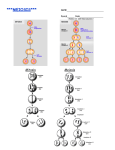
Meiosis: Making reproductive cells Meiosis: the process of nuclear division where the number of the chromosomes is halved. • produces four daughter cells • all daughter cells are haploid (n) • chromosomes are shuffled in the process, so that each daughter cell has a unique combination (it produces many different reproductive cells.) • process that makes gametes (sperm and egg) Crossing-Over - Chromosomes exchange sections - Crossing over increases variability/diversity - Crossing-over increases the already huge number of different gamete types produced by independent assortment Spermatogenesis: Production of male gametes (sperm) Oogenesis: Production of female gametes (eggs) Spermatogenesis Occurs in the testes Two divisions produce 4 sperm cells Men produce about 250,000,000 sperm per day Oogenesis Occurs in the ovaries Two divisions produce 3 polar bodies that die and 1 egg Polar bodies die because of unequal division of cytoplasm Starting at puberty, one egg matures every 28 days Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis vs. Meiosis Mitosis • Cell division of body cells (somatic) • Produces 2 diploid cells (2n) • Each new cell contains copies of all chromosomes • One cell division • All cells are identical (photocopies) Meiosis • Cell division that produces gametes • Produces 4 haploid cells (n) • Each gamete contains just one chromosome of each pair • Two cell divisions • All cells are different (diversity) Fertilization