* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT only
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
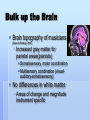
Music Or, a lecture to soothe the savage beast Music Basics What is music? Sound and silence temporally organized Sounds of music Pitch, timbre, loudness Scale Sequential presentation of notes Fundamental = note at scale base, bottom note of chord Chord Collection of notes played simultaneously Timbre and Complexity Harmonics Notes at specific intervals that resonate above a fundamental Vary in loudness Onset, offset time Characteristic harmonics determine timbre Demo 1 - harmonic changes sound (track 53) Harmonics change the sound, NOT the pitch Music Physics Consonance Intervals of notes that when played simultaneously sound good together Synergistic overtones Dissonance (Track 62) Intervals of notes that when played together sound conflicting Interference pattern between overtones Structural Music Scale perception Western Music uses accents to structure sound Asynchronous western scale Whole step, whole step, half step, Whole step, whole step, whole step, half step 8 notes per scale, 16 notes available Causes leading tones Asynchronous scales Whole tone scale Chromatic (half-step scale) Same notes, no structure Music Training Instrument specific Present violin or trumpet to violinist or trumpeter (Pantev et al., 2001) Event related potential (ERP) Pattern, timing of neural response Unspecified region Instrument specific N1 Attention related negativity of neural response Larger for own instrument Brain Changes Hemispheric Differences (e.g., Burton et al., 1989) Musical categorization Left or Right presentation; musician or nonmusician Musician = Right ear advantage; Non=Left ear advantage Hemispheric specialization changes with training Left brain: speech specialization, dynamic processing;Right brain: spatial processing But see Zatorre (1979) Bulk up the Brain Brain topography of musicians (Gaser & Schlaug, 2003) Increased gray matter for parietal areas(pianists) Somatosensory, motor coordination Multisensory combination (visualauditory-somatosensory) No differences in white matter Areas of change and magnitude instrument specific