* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Extra Slides - MAN 341-- Production Management
Channel coordination wikipedia , lookup
Operations management wikipedia , lookup
Business process wikipedia , lookup
Service blueprint wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Market environment wikipedia , lookup
Target costing wikipedia , lookup
False advertising wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
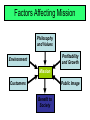
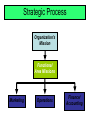
Extra Notes on Strategy Developing Missions and Strategies Mission statements tell an organization where it is going The Strategy tells the organization how to get there Mission Mission - where are you going? Organization’s purpose for being Answers ‘What do we provide society?’ Provides boundaries and focus Factors Affecting Mission Philosophy and Values Profitability and Growth Environment Mission Customers Public Image Benefit to Society Strategic Process Organization’s Mission Functional Area Missions Marketing Operations Finance/ Accounting Strategy Action plan to achieve mission Functional areas have strategies Strategies exploit opportunities and strengths, neutralize threats, and avoid weaknesses Strategies for Competitive Advantage Differentiation – better, or at least different Cost leadership – cheaper Quick response – more responsive Competing on Differentiation Uniqueness can go beyond both the physical characteristics and service attributes to encompass everything that impacts customer’s perception of value Safeskin gloves – leading edge products Walt Disney Magic Kingdom – experience differentiation Hard Rock Cafe – theme experience Competing on Cost Provide the maximum value as perceived by customer. Does not imply low quality. Southwest Airlines – secondary airports, no frills service, efficient utilization of equipment Wal-Mart – small overheads, shrinkage, distribution costs Franz Colruyt – no bags, low light, no music, doors on freezers Competing on Response Flexibility is matching market changes in design innovation and volumes Institutionalization at Hewlett-Packard Reliability is meeting schedules German machine industry Timeliness is quickness in design, production, and delivery Johnson Electric, Bennigan’s, Motorola OM’s Contribution to Strategy Operations Decisions Product Quality Process Examples Specific Strategy Used Competitive Advantage FLEXIBILITY Sony’s constant innovation of new products………………………………....Design HP’s ability to follow the printer market………………………………Volume Southwest Airlines No-frills service……..…..LOW COST Location Layout Human resource Supply-chain Inventory Scheduling Maintenance DELIVERY Pizza Hut’s five-minute guarantee at lunchtime…………………..…..……..Speed Federal Express’s “absolutely, positively on time”………………………..….Dependability Differentiation (Better) Response (Faster) QUALITY Motorola’s automotive products ignition systems…………………………......Conformance Motorola’s pagers………………………..….Performance IBM’s after-sale service on mainframe computers……....AFTER-SALE SERVICE Fidelity Security’s broad line of mutual funds………….BROAD PRODUCT LINE Cost leadership (Cheaper) Figure 2.4 Dynamics of Strategic Change Changes within the organization Personnel Finance Technology Product life Changes in the environment Product Life Cycle Company Strategy/Issues Introduction Growth Maturity Best period to increase market share Practical to change price or quality image Poor time to change image, price, or quality R&D engineering is critical Strengthen niche Competitive costs become critical Defend market position CD-ROM Internet Sales Decline Cost control critical Fax machines Drive-through restaurants Color printers Flat-screen monitors DVD 3 1/2” Floppy disks Figure 2.5 Product Life Cycle OM Strategy/Issues Introduction Product design and development critical Frequent product and process design changes Growth Forecasting critical Product and process reliability Maturity Standardization Less rapid product changes – more minor changes Competitive product improvements and options Optimum capacity High production costs Shift toward product focus Long production runs Limited models Enhance distribution Product improvement and cost cutting Short production runs Attention to quality Increasing stability of Increase capacity process Decline Little product differentiation Cost minimization Overcapacity in the industry Prune line to eliminate items not returning good margin Reduce capacity Figure 2.5 Ranking Corruption Rank 1 2 5 7 9 11 12 15 16 17 17 24 35 64 71 77* Country Finland New Zealand Singapore Switzerland Australia United Kingdom Canada Germany Hong Kong Ireland USA Japan Taiwan Mexico China Turkey 2004 CPI Score (out of 10) 9.7 Good 9.6 9.3 9.1 8.8 8.6 8.5 8.2 8.0 7.5 7.5 6.9 5.6 3.6 Not So 3.4 Good 3.1