* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Management of Infratemporal Fossa Lesions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
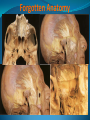
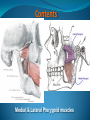
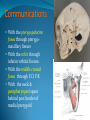
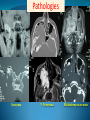
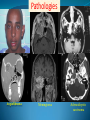
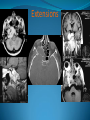
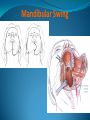
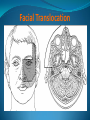
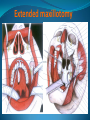
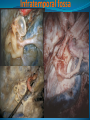
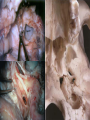
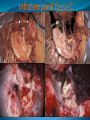
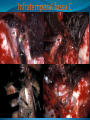
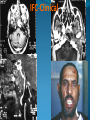
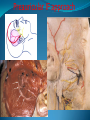
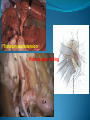
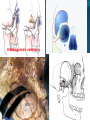
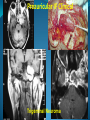
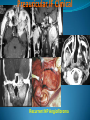
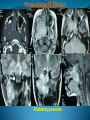
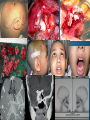
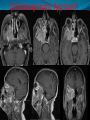
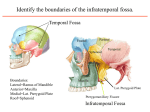
Essam Saleh , MD Prof of Otolaryngology, Alex Univ. Forgotten Anatomy Anatomy Anterior: post.wall maxilla. Posterior: Styloid, Carotid sheath, Condyle Medial: Lat pterygoid plate & sup constrictor. Lateral: Ramus of Mandible Superior: Sphenoid Contents Medial & Lateral Pterygoid muscles Contents Maxillary artery Mandibular nerve Communications With the pterygopalatine fossa through pterygomaxillary fissure With the orbit through inferior orbital fissure. With the middle cranial fossa through F.O, F.R With the neck & parapharyngeal space behind post.border of medial pterygoid Pathologies 1ry: Schwannoma, Rhabdomyosarcoma, Fibrosarcoma, Chondrosarcoma, Hemangiopericytoma, Lymphoma. 2ry extensions from adjacent areas: Adenocarcinoma, Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma, Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Meningioma. Pathologies Sarcoma V Neuroma Rhabdomyosarcoma Pathologies Angiofibroma Meningioma Adenoidcystic carcinoma Problems Deep Location Difficult Access Extensions to more than one anatomical compartment Relations to nearby vital structures: ICA Cavernous Sinus Orbit Extensions Problems Minimal symptoms late diagnosis Difficult to attain preoperative radiological diagnosis. Difficult to have preoperative biopsy. Management Anterior Approaches Transpalatal Lateral rhinotomy Facial degloving. Anterolateral Approaches Extended maxillotomy, maxillectomy, osteoplastic maxillotomy. Maxillary swing. Mandibular swing. Facial translocation. Lateral Approaches Infratemproal fossa type C. Preauricular-infratemporal –subtemporal. Preauricular orbitozygomatic approach. Infratemporal fossa type D. Anterior Approaches Valid only for limited tumor extension into the infratemporal fossa. Minimal control of the vital structures ICA Cavernous sinus. Suitable for primary paranasal sinuses, pterygopalatine fossa & midline clival lesions with minimal lateral extension. Anterolateral Approaches Extended maxillotomy, maxillectomy, osteoplastic maxillotomy. Maxillary swing. Mandibular swing. Facial translocation. Mandibular Swing Facial Translocation Extended maxillotomy Anterolateral Approaches Advantages: Direct access to nasopharynx, pterygopalatine fossa, PNS and clivus. Disadvantages Very extensive. High risk of osteoradionecrosis, oroantral fistula, trismus. Need for tracheostomy. Transgressing contaminated field. Lateral Approaches The preferred routes in our hospital. Concept: direct lateral access to the infratemporal fossa through: Temporalis displacement Transzygomatic. Mandibular retraction and glenoid cavity drilling. Approaches Infratemporal fossa type C Preaucricular infratemporal Infratemporal fossa Infratemporal fossa C Infratemporal fossa C IFC-Clinical Preauricular IF approach Extensions to basic approach Transcervical extension Craniotomy ± transpetrous drilling Orbitozygomatic osteotomy Transcervical extension Petrous apex drilling Orbitozygomatic osteotomy Preauricular IF Clinical Trigeminal Neuroma Preauricular IF Clinical Recurrent NP Angiofibroma Preauricular IF Clinical Rhabdomyosaroma Orbitozygomatic Approach Orbitozygomatic Approach O T Lateral Approaches Advantages Excellent exposure of the infratemporal fossa, pterygopalatine fossa, nasopharynx, sphenoid sinus, posterolateral orbit and inferolateral cavernous sinus. Excellent control of ICA. Can be combined with different approaches transtemporal and transnasal approaches. No facial exposure. Lateral Approaches Disadvantages Sacrifice of the mandibular nerve. Significant CHL in the IF-C approach. Poor control of the other PNS and nasal cavity. Lengthy procedure Infratemporal Fossa Tumors 11 cases (10 males & 1 Female) Age : 9-65 yrs (mean 32.6 yrs). Recurrent NP angiofibroma NP Carcinoma Meningioma Recurrent Chondrosarcoma Trigeminal Neuroma Rhabdomyosarcoma 4 2 2 1 1 1 ] -->1ry Infratemporal Fossa Tumors Extension Pterygopalatine Fossa Cavernous sinus ICA Orbit Sphenoid sinus Clivus (erosion) PNS Petrous apex Parapharyngeal space No(%) 7 (64%) 6 (55%) 5 (45%) 6 (55%) 5 (45%) 4 (36%) 4 (36%) 2 (18%) 2 (18%) Approaches IFC Preauricular IF Preauricular IF + Orbitozygomatic Preauricular IF + Transcx Preauricular IF + Transcx + Transpalatal Preauricular IF + Transnasal Preauricular IF + MF-Transpetrous Transcochlear + Transtent + IF 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 Infratemporal Fossa Tumors Total removal 9 cases (one staged) Recurrence (one case) Post-op Radio ± chemotherapy 2 cases Frontal VII paresis 3 cases. No Mortality Conclusions Infratemporal fossa tumors are difficult to diagnose and manage. Anterolateral approaches afford a direct route with little morbidity and can be combined with different other procedures to achieve a safe and total removal. Adequate knowledge of the anatomy is mandatory before embarking on this difficult surgery. Recurrent irradiated nasopharyngeal tumors can be managed surgically with excellent results for early cases.