* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 Medicine in the countries of Ancient World
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
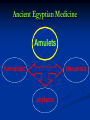
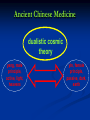
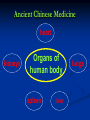
Lecture 2 Medicine of the Ancient World Lecture Plan 1.The Egyptian Medicine. 2.Medicine of the Peoples of Mesopotamia. Babylon and Assyria. 3.Medicine in India. 4.Medicine in China. 5.Ancient Greek Medicine. 6.Medicine in Ancient Rome. Stages in the Development of Medicine •Medicine of the Primitive Society 3,000,000 B.C. – 5,000 B.C. •Medicine of the Ancient World 5,000 B.C. – 476 A.D. •Medicine of the Middle Ages 476 – end of 17th century •Renaissance Medicine 15th century •Early Modern Medicine •Medicine in the 20th Century ANCIENT MEDICINE TIMELINE Egypt 5,000 B.C. prehistoric India 3,000 B.C. China 4,000 B.C. Mesopotamia 3,000 B.C. medieval Mesopotamian Medicine establishment of calendar dawn of recorded history invention of writing Mesopotamian Medicine Scanty evidence •clay tablets bearing cuneiform signs and seals used by physicians of ancient Mesopotamia •the Code of Hammurabi (Babylonian king of the 18th century BC) inscribed on stone pillar, containing laws relating to the practice of medicine, and the penalties for failure Mesopotamian Medicine !notable! every Babylonian was an amateur physician, since it was the custom to lay the sick in the street so that anyone passing by might offer advice Mesopotamian Medicine !notable! divination, from the inspection of the liver of a sacrificed animal, was widely practiced to foretell the course of a disease Ancient Egyptian Medicine Impact • • • • of Magic and Religion Incantations Magical ingredients Selection of remedies or ingredients (simila similibus principle) Amulets Ancient Egyptian Medicine Amulets homopoeic theophoric phylactic Ancient Egyptian Medicine Imhotep • The first physician to emerge in Egypt is Imhotep, chief minister to King Djoser in the 3rd millennium BC, who designed one of the earliest pyramids, the Step Pyramid at Ṣaqqārah, and who was later regarded as the Egyptian god of medicine and identified with the Greek god Asclepius. Ancient Egyptian Medicine Sources of knowledge • • • study of Egyptian papyri study of the artistic representation of disease in the Nile Valley study of human remains of ancient Egyptians Ancient Egyptian Medicine widespread practice of embalming the dead body scarce study of human anatomy Ancient Egyptian Medicine Basic features ranks of doctors specializations in the doctors medical institutions Ancient Indian Medicine Periods Vedic medicine until 800 BC Golden age 800BC-1000AD Ancient Indian Medicine religion prohibited cutting the dead body knowledge of anatomy was limited Ancient Indian Medicine Health of human body spirit (air) phlegm bile Ancient Indian Medicine flesh fat blood Human body bone semen chile marrow Ancient Indian Medicine Surgical operations performed by Hindu surgeons: excision of tumours incision and draining of abscesses punctures to release fluid in the abdomen extraction of foreign bodies repair of anal fistulas splinting of fractures amputations caesarean sections stitching of wounds Ancient Indian Medicine Outstanding operations performed by Hindus removal of bladder stones by lateral lithotomy Ancient Indian Medicine Outstanding operations performed by Hindus PLASTIC SURGERY. Amputation of the nose and repair by cutting a piece of tissue from the patient's cheek or forehead and applying it to the stump of the nose Ancient Chinese Medicine dualistic cosmic theory yang, male principle, active, light, heavens yin, female principle, passive, dark, earth Ancient Chinese Medicine wood water Human body metal earth fire Ancient Chinese Medicine heart kidneys Organs of human body spleen liver lungs Ancient Chinese Medicine intestines gallbladder Viscera of human body stomach bladder Ancient Chinese Medicine Basic features Hydrotherapy Acupuncture Moxibustion Ancient Greek Medicine Asclepius The divine Asclepius, the god of medicine, may have originated in a human Asclepius who lived about 1200 BC and is said to have performed many miracles of healing. Ancient Greek Medicine Temple medicine Diet Bath Exercises Ancient Greek Medicine In the 5th century BC Empedocles set forth the view that the universe is composed of four elements—fire, air, earth, and water; this conception led to the doctrine of the four bodily humours: blood; phlegm; choler, or yellow bile; and melancholy, or black bile. The maintenance of health was held to depend upon the harmony of the four humours. Ancient Greek Medicine The equilibrium of the four humours: black bile yellow bile (red) blood (green) phlegm Ancient Greek Medicine Hippocrates: Epilepsy “is not any more sacred than other diseases, but has a natural cause, and its supposed divine origin is due to man's inexperience. Every disease has its own nature, and arises from external causes.” Ancient Greek Medicine Hippocratic an oath ethical code, an ideal, an appeal for right conduct Ancient Rome Medicine good hospitals unrivalled water supply Basic features domestic sanitation adequate disposal of sewage Дякую за увагу! Thank you for your attention! Merci de votre attention! Dziękuję za uwagę! Danke für Ihre Aufmerksamkeit!