* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture4
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
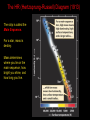
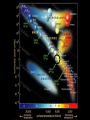
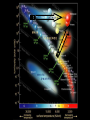
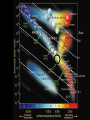
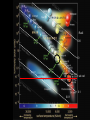
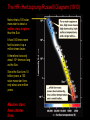
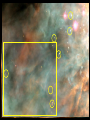
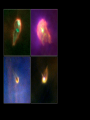
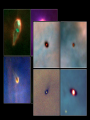
Lecture 4: The Life-Cycles of Stars Astronomy 5: The Formation and Evolution of the Universe Sandra M. Faber Spring Quarter 2007 UC Santa Cruz The visible-light spectrum of the Sun is wrapped here end to end from red to blue. The dark “lines” are wavelengths that are absorbed by atoms in the Sun’s outer layers. There are millions of “lines” in the Sun’s spectrum. H The strengths of the lines are related to the number of atoms of each element. Na Mg Modeling these features allows us to measure the Sun’s composition. H Na Mg The simplest nuclear reaction that makes stars shine The HR (Hertzsprung-Russell) Diagram (1913) The strip is called the Main Sequence. For a star, mass is destiny. Mass determines where you lie on the main sequence, how bright you shine, and how long you live. Radii 100 10 1 sol rad 0.1 0.01 Radii 100 10 1 sol rad 0.1 0.01 The HR (Hertzsprung-Russell) Diagram (1913) Notice that a 100 solar mass star is about a million times brighter than the Sun. It has 100 times more fuel but uses it up a million times faster. It therefore lives only about 10-4 times as long as the Sun. Since the Sun lives 10 billion years, a 100 solar mass star lives only about one million years. Massive stars have shorter lives. A star cluster of 10,000 stars all formed at the same QuickTime™ and a time. The HR diagram evolving with time. YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. One of the most famous diagrams in astronomy: a collection of HR diagrams for star clusters of different ages. Stellar populations in the Andromeda galaxy Red bulge, “red and dead” Blue disk, star forming Star forming regions in M33, a small spiral neighbor of the Andromeda galaxy Stars form from dense clouds of gas Messier 33 galaxy, a nearby member of the Local Group The Orion Nebula: a typical H II region* * H II means hydrogen is ionized, H I means neutral. H II glows in visible light, H I emits only radio waves. In the heart of the Orion Nebula… In the heart of the Orion Nebula… Flying through the center of the Orion Nebula QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video decompressor are needed to see this picture. 17 times Pluto’s orbit Orion “proplyd” A rotating proto-solar nebula: “rocks” seem to be the seeds of planets QuickTime™ and a MPEG-4 Video decompressor are needed to see this picture. Supernovae seed the interstellar gas with heavy elements, which are the “ashes” of nuclear burning. They come from massive stars, above 8 solar masses. C N O Si Fe The Crab nebula supernova remnant etc... Order these star clusters by age A major recent discovery: color bimodality A major recent discovery: color bimodality A major recent discovery: color bimodality