* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sun 2013
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Interstellar probe wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
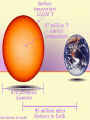
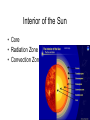
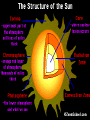
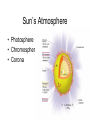
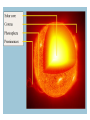
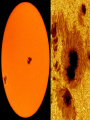
+ The Sun Sun Facts Makes life on our planet possible by giving us great amounts of light and heat Contains about 98% of the mass of the entire Solar System. Is just a medium sized star (yellow dwarf). Is the center of our Solar System. All the planets and other objects orbit around it. Contains dark spots that are known as Sun Facts • The Sun is a ball of hot gases: mostly hydrogen and helium • The average distance from the Earth to the Sun is 93,000,000 miles. • It takes light eight and a half minutes to travel from the Sun to the Earth. • The diameter of the Sun is 870,000 miles, 109 times larger than the Earth's. Its volume is big enough to hold over 1 million Earths. Interior of the Sun • Core • Radiation Zone • Convection Zone Interior of the Sun • Core – Energy is produced in the core by nuclear fusion – Nuclear Fusion is the process of hydrogen atoms joining together to form helium – Very extreme temperatures at the core Nuclear Fusion • The Sun converts 600 million tons of hydrogen into 596 million tons of helium every second. The extra 4 million tons is converted into energy Radiation Zone • Middle layer • Energy is transferred in the form of electromagnetic radiation Convection Zone • Outermost layer • Temperature of gases cool as it reaches the top of the convection zone • Convection*** Remember this term???? • Heat transfer through a fluid (gases are fluids) Sun’s Atmosphere • Photosphere • Chromosphere • Corona Photosphere • Inner layer of sun’s atmosphere • Photo=light • Sphere that gives off visible light Chromosphere • • • • Middle layer of sun’s atmosphere Chroma=color Color sphere Reddish glow Corona • • • • • White halo around the sun Corona=crown Seen during a total solar eclipse Outer layer of sun’s atmosphere Corona extends into space for millions of kilometers and gradually thins into streams of electrically charges particles called the solar wind Solar Wind=1 million mph • The source of the solar wind is the Sun's hot corona. The temperature of the corona is so high that the Sun's gravity cannot hold on to it. • Solar flares can greatly increase the solar wind from the corona=increase in the number of particles reaching Earth’s upper atmosphere Features on the Sun • Sunspots • Prominences • Solar Flares Sunspots • Dark spots on the sun’s surface • Areas of gas on the sun’s surface that are cooler than the gases around them • Cooler gases don’t give off as much light as hotter gases • The number of sunspots varies over a period of about 11 years • Increase in sunspot activity=Increase in magnetic storms Prominence • Reddish loops of gas that often link different parts of sunspot region Solar Flares • Eruptions of magnetic energy Auroras • When particles enter they create powerful electric currents that cause gas molecules to glow=auroras • Solar wind particles can also affect Earth’s magnetic field, causing magnetic storms • Magnetic storms can disrupt radio, telephone, and TV signals