* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 Lesson 1: The Sun
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
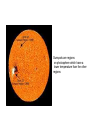
Chapter 5 Lesson 1: The Sun What is the Sun? • A star which produces its own energy (light) • There are stars which can make ten million times what the sun makes • Our sun is an average sized star • Our sun can hold more than a million earths The sun is made of mostly two gases, hydrogen and helium Sunspots are regions on photosphere which have a lower temperature than the other regions What are the parts of the sun? -Radiation layer next to core moves energy in all directions -Convection layer gases move in circles -Photosphere is visible surface -Chromosphere inner layer of the sun’s atmosphere, red circle around sun -Corona outermost layer Solar flares are bursts of heat and energy coming off the sun How does the sun produce energy? • Albert Einstein discover relationship between energy and mass • E=mc2 • E energy, m mass, c speed of light Inside the sun, hydrogen particles smash together to make helium (fusion) Review Questions • What is the largest object in our solar system? • An object in the solar system that produces heat and light is a _______________. • What causes energy to be released inside the sun? • How would earth be affected if the sun stopped producing energy? • Why are the planets not stars? • Why do you think it take millions of years for energy that moves in every direction to leave the radiation layer? • What happens when hydrogen particles collide?