* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Brown dwarf wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
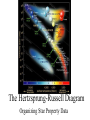
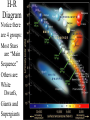
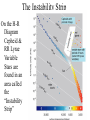
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Organizing Star Property Data The H-R Diagram The “H-R” Diagram was invented around 1910 to organize stars based on their properties. The diagram is a graph. Vertically the scale is increasing Luminosity Horizontally the scale is Spectral Class/Temperature From Hot (O class) to Cool (M class). H-R Diagram Notice there are 4 groups: Most Stars are “Main Sequence” Others are: White Dwarfs, Giants and Supergiants About the Groups Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ stars are hotter…and thus ‘burn’ fuel fast, and have short lives White Dwarfs are hot, but not that bright, so they must be small. Giants and Supergiants are cool, but bright so they must be very large. The Instability Strip On the H-R Diagram Cepheid & RR Lyrae Variable Stars are found in an area called the “Instability Strip”