* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Relative sizes of astronomical objects
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
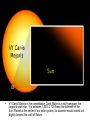
This is a representation of Earth relative to the rocky inner planets and the outermost dwarf planet Pluto. Note the difference in size between the gas giants (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus & Neptune) and the rocky inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth & Mars) • Viewed in comparison to the Sun, Earth dwindles to a speck. Our sun is classified as an unremarkable yellow dwarf main sequence star – one of over 100 million such stars in our galaxy. However, it alone accounts for 99.9% of the mass of our solar system, including all the planets, satellites (moons), asteroids, and interplanetary debris. • When compared it to some other stars, our Sun dwindles to the size of a corn kernel. This image represents the relative sizes of our Sun and Sirius (Alpha Canis Majoris), Pollux (Beta Geminorum) and Arcturus (Alpha Bootes). ‘Giant’ Jupiter is just 1 pixel in this perspective. Earth is invisible on this scale. • In this comparison our Sun is down to 1 pixel, a mote of dust with an arrow pointing to it. Jupiter is invisible. Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis) is a red supergiant. If Betelgeuse replaced our Sun, its surface would lie between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. Antares (Alpha Scorpii) is a red supergiant 700 times the diameter of our Sun. The three stars noted below Antares are Sirius, Pollux and Arcturus. • VY Canis Majoris in the constellation Canis Major is a red hypergiant, the largest known star. It is between 1,800–2,100 times the diameter of the Sun. Placed at the center of our solar system, its diameter would extend out slightly beyond the orbit of Saturn. • And yet these are but just a few of the thousands of millions of stars in the Milky Way! To comprehend the cosmic significance of our galaxy ... • We finally turn to this Hubble Ultra-Deep Field image, a composite of pictures taken in the constellation Fornax, September 2003-January 2004. The image covers just 11.0 square arcminutes, smaller than a 1 mm-by-1 mm square of paper held 1 meter away. Yet each one of those smudges is a galaxy. Some 10,000 of them have been counted in this image alone.