* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download January 14 - Astronomy
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
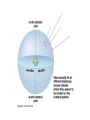
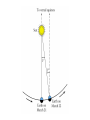
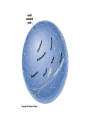
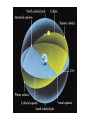
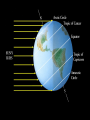
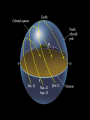
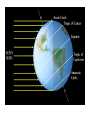
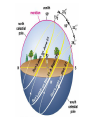
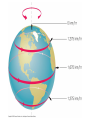
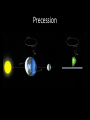
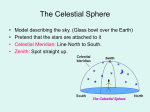
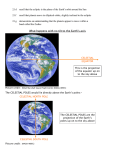
The Night Sky Discussion Describe how the stars move in the sky as viewed from the Earth’s north pole. Where in the sky is the north celestial pole, the south celestial pole and the celestial equator? Discussion Describe how the stars move in the sky as viewed from the Earth’s equator. Where in the sky is the north celestial pole, the south celestial pole and the celestial equator? Discussion Describe how the stars move in the sky as viewed from a latitude of 35 degrees north. Where in the sky is the north celestial pole, the south celestial pole and the celestial equator? North celestial pole South celestial pole What is the latitude of this picture? Discussion Which star (A, B, C, or D) will spend the least amount of time above the horizon during the course of a day? How long do stars on the celestial equator spend above the horizon? If taken in the northern hemisphere, are the stars rising or setting in this picture? Discussion What is the difference between the solar day and the sidereal day? Solar and sidereal days Solar day – 24 hours is the average time between two solar meridian crossings Sidereal day – 23 hours 56 minutes is the actual rotation period of the Earth Discussion What is the ecliptic? The ecliptic The ecliptic is the annual path through the sky that the Sun appears to take. In other words, the ecliptic is the plane of Earth’s orbit projected onto the stars. The constellations Traditionally, a constellation is a grouping of stars in the same part of the sky. Orion The constellations In modern astronomy, the constellations are 88 irregular areas that completely cover the sky. Thus, every celestial object lies within the boundaries of a constellation. Ursa Major Discussion Why do you think ancient astronomers invented the constellations and made up stories to go with them? Canis Major Constellations of the Zodiac The ecliptic passes through 12 constellations (actually 13) during the year. This are know as the zodiacal constellations. Discussion About what time is it in this picture? Discussion In what constellation will the Sun be in at 6 pm? Discussion In what constellation will the Sun be in one month from the time of this picture? The Seasons Due to the Earth’s rotation axis being tilted by 23.5 degrees from perpendicular to the plane of its orbit. Near edge-on view Conservation of angular momentum Anything that spins on an axis or revolves around another object has angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum requires that the rate of spinning remains constant with time. Also, the axis of rotation of any spinning object remains in a fixed direction in space. Discussion Why is it hard for people to learn to ride a bike, but once they learn it is considered easy? Discussion Where is the Sun today on the previous picture? The seasons and ellipticity The Earth’s orbit is nearly circular – distance from the Sun varies by only 3% Earth is closest to the Sun in January and furthest from the Sun in July Summer in northern hemisphere is winter in southern hemisphere Why is summer warmer? 1. The Sun, being above the celestial equator, remains in the sky longer during the summer, the longest daylight time occurring on the summer solstice. 2. The Sun rays hit the earth more directly during the summer months, i.e. the summer hemisphere receives more energy per square meter. Discussion If the Earth’s rotation axis were exactly perpendicular to the ecliptic, would we still experience seasons? Which planet has most the extreme seasons? Discussion Another student tells you that the seasons are caused the Earth being closer to the Sun in the summer and farther from the Sun in the winter. What evidence could you use to refute this claim? The arctic circle The arctic circle is the northern latitude at which on the summer solstice the Sun never sets and on the winter solstice the Sun never rises above the horizon. Discussion The tropics mark the farthest points north and south where the Sun can appear at the zenith. What is the latitude of the tropics? Discussion What is the latitude of the arctic circle? Discussion From Cleveland on the vernal equinox, describe how the sun moves through the sky during the course of a day. (Where does it rise, where does it cross the meridian, and where does it set.) Discussion From Cleveland on the first day of summer, describe how the sun moves through the sky during the course of a day. Discussion From Cleveland on the first day of winter, describe how the sun moves through the sky during the course of a day. Precession: a complication The Earth’s rotation axis is not fixed in space over long periods of time The Earth’s rotation rate is nearly constant, its speed is not The speed at which points on the Earth’s equator are moving is larger than points on the Earth at higher latitudes. At the equator you would be moving at 1,650 km/hr, while at the north pole you would not be moving at all, just rotating around a point. Discussion Why is Kennedy Space Center in Florida and not in Maine? Florida is closer to the equator and a space shuttle just sitting on the launch pad is moving about 1,550 km/hr. If we moved the launch pad to Maine, the space shuttle sitting on the launch pad is only moving 1,275 km/hr or about 275 km/hr less than in Florida. To launch the space shuttle in Maine would require more fuel to accelerate the shuttle the extra 275 km/hr. Equatorial Bulge The extra velocity at the equator pushes the matter out at the equator. The same thing happens on a merry-go-round. The closer you are to the edge, the faster you will be moving, and the greater the force pushing you off. The Earth is not a perfect sphere The Earth bulges out at its equator, that is, its diameter measured along its equator is 43 km larger than its diameter from the north to the south pole. Oblateness Precession The Sun and Moon apply a torque to the Earth Because the Earth is not a perfect sphere and its rotation axis is tilted 23.5 degrees from its orbital plane, the Sun and the Moon pull on the extra mass in Earth’s equatorial bulge and try to straighten out the tilt. Precession This off axis force, or torque on the Earth causes Earth’s rotation axis to vary slightly, or precess, over long periods of time. Thus, the celestial poles trace out a circle against the stars over a period 26,000 years. Discussion The Great Pyramid at Giza has a tunnel which points toward the north celestial pole. At the time the pyramid was built, around 2600 BCE, toward which star did it point?