* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3observing3s
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Epoch (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
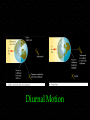
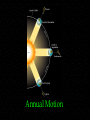
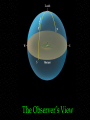
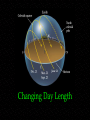
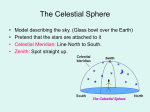
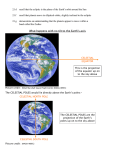
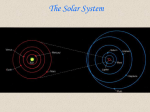
Observing and the Sky Astronomy 311 Professor Lee Carkner Lecture 3 Our Point of View Think about the motions of the heavens from different points of view Remember that everything is moving at once The Changing Sky Sky makes one complete rotation per 24 hours (Diurnal motion) Sky also makes one complete rotation per year (Annual motion) Caused by the motion of the Earth around the Sun Diurnal Motion Annual Motion The Observer’s View Observing Can measure distance on the sky in degrees (360 degrees = complete circle) Horizon -Zenith -Meridian -- line running from north to south through zenith The Solar Year The Seasons When the northern hemisphere is pointed at the Sun, it is summer here Seasons are not caused by Earth being more or less distant from the Sun!!! Direct and Indirect Sunlight Solstice Equinox When the Sun is highest or lowest in the sky When the Sun is overhead at the equator Longest or shortest day of year Day and night equal in length Changing Day Length Lines on a Globe Equator -Tropic of Capricorn -- 23 1/2 degrees south of the equator, Sun overhead on Winter solstice Tropic of Cancer -- Arctic and Antarctic Circles -- 23 1/2 degrees south or north of the pole, Sun never sets or rises at solstice time Equal to the angle of Polaris above horizon Longitude (degrees East or West of the Prime Meridian running through Greenwich England) Navigation The Celestial Sphere Project the lines on a globe into space to form a coordinate system North Celestial Pole -- Celestial Equator -Project the Earth’s equator into space Celestial Coordinates Right Ascension -- degrees east from where the sun is on the Vernal Equinox (first day of spring) Declination -- The coordinates do not move or vary with location on the Earth, they are fixed to the stars The Ecliptic Most of the objects in the solar system have their orbits in the same plane, called the ecliptic The ecliptic passes through 12 constellations known as the zodiac Constellations of the Zodiac Precession The Earth “wobbles” as it spins, causing the Earth’s axis to point at different parts of the sky This changes where the equinoxes are in the sky Astrology Your sign is supposed to be where the Sun was on the zodiac when you were born For example: Sept 10th = Virgo, but Sun is in Leo. All star signs are about 1 month off Science and Pseudoscience Astronomy is a science, it tries to form a picture of the universe based on observation and reason. It is subject to proof Astrology is a pseudoscience, it uses some of the terminology of science, but its basic tenets are not subject to proof Next Time Meet back in Science 102 on Monday Read Chapter 1.6