* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy - Wappingers Central School District
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
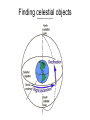
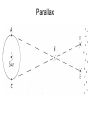
Astronomy: Here is my powerpoint from last years coaches conference. I will be updating it to reflect the changes in content in this years rules. I’m not sure yet how to test 50 teams at States on the use of DS9 image viewing software, and won’t use it at all for regionals. Finding celestial objects (hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu) Finding celestial objects ( burro.cwru.edu) Parallax Parallax Stellar parallax: angle abc Parallax angle: ½ angle abc Parsec: distance to a star with 1” parallax angle Parsec: ~31 trillion km (19 trillion miles) Parsec: 3.26 light years Parallax Star's distance (pc) = 1 / parllax (“) Useful for stars up to about 100pc Magnitude Apparent magnitude (m) Hipparchus 1 to 6 Lower numbers brighter Absolute magnitude (M) Corrected to standard distance of 10pc Can be determined form spectra Distance modulus: m – M Hertzsprung & Russel; not vampires Stellar Motion Red shifting (from the corner of her mouth) Hubble Constant v = Hd Ho = ~ 74 km/sec/Mpc (~ 23 km/sec/MLY) Age of universe v = Hd H = v/d 1/H = d/v = time 1/Ho = age of the universe Schwarzschild radius (Rs) Radius to become a black hole Rs = 2GM/c2 G = gravitational constant M = mass of the body C = speed of light Object > 3 solar masses become black holes Wien & Stefan-Boltzman λmax = 0.3/T T = temperature in Kelvin Total energy emitted is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute temperature A star 2x sun's temperature emits 16x more energy 24 = 16 Open Clusters 100 to 10,000 loosely packed Concentrated in spiral arms Young Hot Highly luminous Like certain vampires Globular Clusters In halo around galactic disk 100,000 to 1 million tightly packed stars Old stars (like Lon Chaney Jr) Population I Stars Hottest & brightest young In disc, spiral arms Relatively high in heavier elements In dust and gas formed from Population II Stars Galactic nucleus and halo Older Almost entirely H & He Classification of Galaxies Galaxy Classifications Elliptical practically all old stars Some gas and dust Normal Spiral and Barred Spiral Various ages Lots of gas and dust in the disk Irregular Mostly young bright stars, ionized gas More Galaxies Lenticular Bright, flat disc No arms No recent stars Dwarf Low mass and luminosity Active Galaxies AGN emits lots of energy Black hole? Distances Cephid variables Standard galaxies Tully-Fisher Relation? 21cm spectral line width Luminosity of spiral galaxies Galaxy Clusters Regular Compact, high density center Mostly elliptical and lenticular Many with active galaxy emition Irregular Our local group Looser structure, little central density Spirals and irregulars Super clusters On edges of voids Featured Objects Where are they What are they Special characteristics? Images?