* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Life Cycle of Stars
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
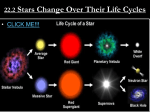
The Life Cycle of Stars This is the death of a star (supernova) viewed by Tycho 400 years ago it was so bright you could see it with the naked eye The Life Cycle of Stars Nebula AAAAA BBBBBB CCCCCCC DDDDDDDD EEEEEEEEE FFFFFFFF The Life Cycle of Stars Nebula Main Sequence Star Red Giant White Dwarf Supernova Neutron Star Black Hole All stars begin as a ball of gas & Dust in space Nebula The stage of our SUN Venus and the International Space Station crossing the sun. Has a Temp. Near 5,000 Nuclear fusion occurs at the core converting Hydrogen to Helium. A star’s longest stage. -6,000 C Main Sequence Star The stars expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. Red Giant Has a Temp. Near 10,000 C Left over centers of old stars remain at this stage. These are small hot stars near the end of their life. White Dwarf This is the death of a large star by explosion Generates a HUGE amount of light, brighter than a whole Galaxy, and may be seen with naked eye. Supernova The materials are squeezed together so hard by gravity electrons and protons become neutrons. Neutron Star Left over from a supernova and very massive So massive light can not escape. The mass of 3 suns and about 6 miles across Black Hole