* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stars, Galaxies & Universe
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
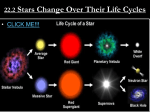
Stars, Galaxies & Universe Chapter 3 1 Tools of Astronomy • Constellations are groups of stars that form a pattern. • The electromagnetic spectrum is made of radio waves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, xrays, and gamma rays. 2 Refracting Telescope • Refracting telescope collects light using lenses. • The lenses bend the light to the focal point. 3 Reflecting Telescope • Reflecting telescope uses a mirror to collect the light. • A concave mirror bends the light inward to a focal point. 4 Radio Telescope • Radio telescopes collects radio waves. • The collector is a concave dish. 5 Observatory • The building that houses a telescope is called an observatory. 6 Other Tools of Astronomy • Telescopes have been put into space on satellites & space stations. • Spectrographs gather information about stars such as a star’s composition & temperature. 7 Characteristics of Stars • A galaxy contains hundreds of billions of stars. • The universe contains billions of galaxies. 8 Distances to Stars • A light year is the distance light travels in year. • Astronomers often use parallax to measure distances to nearby stars. • Parallax is the apparent change in position of an object when you look at it from different places. 9 Classifying Stars • Stars are classified by size, temperature, and brightness. • Temperature of a star is indicated by color, hot stars are blue & cooler stars are red. • Apparent brightness is the brightness of a star as observed from earth. • Absolute magnitude is the brightness of a star observed at the distance of 10 parsecs. 10 Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • H-R diagram is a graph of the Milky Way galaxy. • Surface temperature is graphed on the xaxis. • Absolute magnitude is graphed on the yaxis. 11 Types of Stars • Blue super giants have a high brightness and high temperature. • Red giants & super giants have a high brightness and low temperature. • White dwarfs have a low brightness and high temperature. • 90% of all stars appear on the Main Sequence going from the upper right to the lower left corner. 12 Birth of a Star • A star begins as a cloud of gas and dust called a nebula. • Gravity pulls the gas and dust together into a protostar. • A star is born when the contracting gas and dust becomes so hot that nuclear fusion begins. 13 Length of Life of a Star • More massive stars live short lives of millions of years. • Less massive stars live long lives of billions of years. • The sun will live for 910 billion years. 14 During the Life Cycle of a Star • Stars fuse hydrogen into helium during most of their lives. • After all the hydrogen has been fused into helium, the star fuses helium into carbon, carbon into oxygen and then oxygen into iron. 15 Death of a Star • Stars use up their hydrogen and expand their atmosphere. • Stars that are less than 1.4 solar masses will shrink to a white dwarf. • Stars between 1.4 -3.0 solar masses will produce a supernova and leave a neutron star. • Stars more than 3.0 solar masses will produce a supernova and collapse into a black hole. 16 Star Systems • Most stars are members of groups of two or more stars called star systems. • Star systems with two stars are called double stars or binary stars. • Binary eclipsing stars are stars where one star blocks the light from another. 17 One of the greatest advancements in astronomy was the telescope. Which is the correct order of advancements? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 12 13 14 15 16 18 0 gre fr ... -.. . g ad io - re fle c ti n ct in ti n. .. ti n ef ra c R 17 0 gre fl e fr ac re g ct in R ef le io ad R 11 0 – re fr ac ti n gre fl. .. 0 R A. Radio- refractingreflecting B. Reflecting – refracting –radio C. Refractingreflecting-radio D. Radio- reflectingrefracting 19 20 18 Why do astronomers measure interstellar distances in light years instead of kilometers or miles? 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 0 ... . on ’t h av e a cl ue .. er s a. . 0 ki lo m et er s M ile s an d M ile s an d ar e ar s ye gh t Li 1 0 a. . 0 a D. ... C. ki lo m et B. Id Light years are a measure of time. Miles and kilometers are too small of a unit. Miles and kilometers are too large of a unit. I don’t have a clue . . . help me! m ea A. 18 19 20 19 Which of the following correctly shows the age progression of an average star? A. Main sequence→White Dwarf→Red Giant →Nebula Red Giant →White Dwarf →Main Sequence →Nebula Nebula →Main Sequence →Red Giant →White Dwarf White Dwarf →Red Giant →Main Sequence →Nebula B. C. D. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 20 What is the next likely stage of a protostar? 0 a 0 N M ai n eu Se tro n qu en ov N ia n Su pe rG 0 St ar 0 ce Super Giants Nova Main Sequence Neutron Star ts A. B. C. D. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Galaxies • • Galaxies are a group of billions of stars. Type of galaxies are 1. Elliptical 2. Spiral 3. Irregular 22 Elliptical Galaxy • Old galaxy. • Contains red star that are old. • No gas or dust. 23 Spiral Galaxy • Middle aged galaxy. • Contains blue stars. • Has some dust and gas. • Our Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. 24 Irregular Galaxy • Unorganized collection of stars. • Made of very young stars. • Has a great deal of gas and dust. 25 History of the Universe • Edwin Hubble discovered that the farther away a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away from us. • Stars moving away from us shows a red shift. 26 Big Bang Theory • Big Bang Theory suggest that billions of years ago, the universe was small, hot and dense and then the universe exploded. • The universe formed in this enormous explosion about 10 to 15 billion years ago. 27 Formation of the Solar System • The solar system formed 5 billion years ago. • The solar system formed from a giant cloud of gas and dust, or nebula. 28 Future of the Universe • The universe may continue to expand. • Gravity may pull the universe back together. 29 What type of galaxy is shown in the picture? A. Irregular 0 B. Spiral 0 C. Elliptical 0 D. I have no idea … I need help!!! 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 30 Review Questions • What are the three types of galaxies? • elliptical, spiral & irregular • Distances between stars are measured in units called _______. • light years • Stars begin as a cloud of gas & dust known as a __________. • nebula 31 Review Questions • What does the length of life of a star depends on? • mass of the star • What is the name of our galaxy? • Milky Way • What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? • spiral • What is the name of the theory of the creation of the universe? • Big Bang 32 Review Questions • What type of tools are used to study the universe? • telescope • Which type of telescope uses mirrors? • reflecting • Which type of telescope uses lenses? • refracting 33 Review Questions • What indicates how hot a star is? • color of the star • During nuclear fusion, what does hydrogen fuse into? • helium • What is graphed on the H-R diagram? • brightness & temperature 34 Review Questions • What is the brightness of a star as seen from earth? • apparent brightness • What is the brightness of a star that is seen at a standard distance of ten parsecs? • absolute magnitude 35 Review Questions • What process is used to measure the distance of nearby stars? • parallax • What type of telescope collect electromagnetic waves other than light? • radio telescope • How long ago did the Big Bang occur? • 10-15 billion years ago 36 Review Questions • • • • • What are patterns of stars in the sky called? Constellations What is the building called that has a telescope? Observatory Which type of galaxy has red stars and no gas or dust? • elliptical 37 Review Questions • Which type of galaxy has blue stars and some gas & dust? • spiral galaxy • Galaxies are classified by their _______. • shape • Who proposed that the universe is expanding? • Hubble 38 Review Questions • What evidence do we have that the universe is expanding? • red shift • What happens to a small star at its death? • white dwarf • What happens to a very large star at its death? • Supernova to a black hole 39 Practice Extended Answer Questions • Describe the life cycle of a star. • What are the three types of telescopes and how are they different? • Explain the H-R diagram. • How does the mass of a star affect the length of life of a star? • How do the different types of galaxies compare? • Explain the Big Bang Theory. 40