* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gravity
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
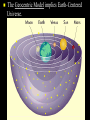
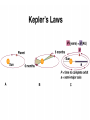
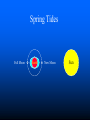
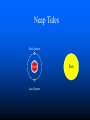
Chapter 9 & 10 Gravity Pythagoras (550 BC) Claimed that natural phenomena could be described by mathematics Aristotle (350 BC) Asserted that the universe is governed by physical laws The ancient Greeks believed that the earth was at the center of a revolving sphere with stars on it. The Geocentric Model implies Earth-Centered Universe. Copernicus (1500's) Developed a mathematical model for a Sun-centered solar system Tycho Brahe (1500's) Made precise measurements of the positions of the planets Kepler (1600's) Described the shape of planetary orbits as well as their orbital speeds Kepler’s First Law The orbit of a planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. Kepler’s Second Law A line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. Kepler’s Third Law The square of a planet's orbital period is proportional to the cube of the length of its orbit's semimajor axis. Or simply… T2 = R3 if T is measured in years and R is measured in astronomical units. An Astronomical Unit... …is the average distance of the Earth from the Sun. 1 AU = 93,000,000 miles = 8.3 lightminutes Kepler’s Laws These are three laws of physics that relate to planetary orbits. These were empirical laws. Kepler could not explain them. Kepler’s Laws...Simply (See page 192.) Law 1: Elliptical orbits… Law 2: Equal areas in equal times… Law 3: T2 = R3 Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation From Kepler's 3rd Law, Newton deduced inverse square law of attraction. Gm1m 2 F 2 d G=6.67 10-11 N m2/kg2 Gravity Questions Did the Moon exert a gravitational force on the Apollo astronauts? What kind of objects can exert a gravitational force on other objects? The constant G is a rather small number. What kind of objects can exert strong gravitational forces? Gravity Questions If the distance between two objects in space is doubled, then what happens to the gravitational force between them? What is the distance is tripled? …is quadrupled? What if the mass of one of the object is doubled? …tripled? …quadrupled? Weight and Weightlessness Weight » the force due to gravity on an object » Weight = Mass Acceleration of Gravity »W=mg Weightlessness - a conditions wherein gravitational pull appears to be lacking – Examples: » Astronauts » Falling in an Elevator » Skydiving » Underwater Ocean Tides The Moon is primarily responsible for ocean tides on Earth. The Sun contributes to tides also. What are spring tides and neap tides? Spring Tides Full Moon Earth New Moon Sun Neap Tides First Quarter Earth Last Quarter Sun End of Section… Einstein’s Theory of Gravitation Einstein perceived a gravitational field as a geometrical warping of 4-D space and time. BLACK HOLES Let’s observe a star that is shrinking but whose mass is remaining the same. What happens to the force acting on an indestructible mass at the surface of the star? SFA F F F m m 1 2 m1m2 F G 2 G Remember that the force between R 2 the two masses is given by R G G m1m2 R2 R m1m2 R2 R R R F G m1m2 R2 BLACK HOLES If a massive star shrinks enough so that the escape velocity is equal to or greater than the speed of light, then it has become a black hole. Light cannot escape from a black hole. Near a Black Hole