* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ASTRONOMY
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
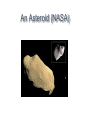
WHAT IS IT? • The study of the night sky and the celestial objects that exist. Let’s take a vacation to…. • If we could travel at the speed of light, 300 000 000 m/s (or 300 000 km/s) • Note: Sound travels at 300 m/s It would take 1 s to get to the 8 minutes to get to the 4 light years to get to 2.5 million light years to get to • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HEhe h1BH34Q&feature=related • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HEhe h1BH34Q&feature=related ASTRONOMY • The study of the night sky and the CELESTIAL objects that exist. • CELESTIAL means sky. Astronomy • The study of the night sky and the CELESTIAL objects that exist. • CELESTIAL means sky. UNIVERSE • All MATTER and ENERGY that exist everywhere. CELESTIAL OBJECTS: • • • • Sun Moon Planets Stars OUR SOLAR SYSTEM • The system of planets and other objects that orbit the Sun in a circular pattern. • The force of GRAVITY is a force of attraction between masses. • The Sun has a very large mass and therefore a strong force of gravity that pulls on the Earth and the other planets, keeping them in orbit. INNER PLANETS Mercury Venus Earth Mars OTER PLANETS Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Remember the planets My very Excited Martian just sent us nachos Planets move in 2 ways: 1. ORBITAL PERIOD the length of time required to orbit the Sun. Eg) Earth’s orbital period = 365.25 days (1 year = 365 days, every 4 years we have a leap year) 2. ROTATIONAL PERIOD the length of time required to rotate on its axis (like a globe) Earth’s Rotation Period = ____________ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lkWyMM8o0c&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R2lP14 6KA5A&feature=related • http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cf m?method=cResource.dspView&Resour ceID=441 The Reason for the Seasons • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DuiQv PLWziQ&safety_mode=true&persist_saf ety_mode=1 • Hmmmm….. Summary • It is because of Earth’s tilt. It is tilted 23.5 degrees from the vertical. In the summer, the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun and receives more direct sunlight making it warmer. In the winter, the N.H. is tilted away from the Sun and receives less sunlight making it cooler. THE SUN • Closest star to Earth. • It is important because it supports life. • Provides us with HEAT and LIGHT, and plants use the energy from the Sun to make FOOD and OXYGEN. • Made up of the gases HYDROGEN and HELIUM. ASTEROIDS • “Large, space rocks” that orbit the Sun. • Found in the ASTEROID BELTbetween Mars and Jupiter. • Range in size (diameter) from a grain of sand to 500 km. • Composed of elements: Iron, carbon, and nickel An Asteroid (NASA) Meteor Sighting • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CgQS x-CO8C8&NR=1 • http://www.cbc.ca/technology/story/2008/ 11/28/meteorite.html • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=18Glk V73VjI What came first? 2 3 Hoba – Africa, largest meteorite (60 tons), 80 000 years ago, About 3 m X 3 m 1 http://www.meteorcrater.com/ METEOROIDS, METEORS, METEORITES • Meteoroids – small “space rocks” that move through space. • They enter Earth’s atmosphere rub against gas particles in the atmosphere become very hot burn up. They can be seen as a flash of light in the night sky, often called “SHOOTING STARS” or METEORS. • If they are large enough they will not completely burn up and a METEORITE will be left on Earth. Sometimes it can make a CRATER from its impact. METEOROITES, METEOROIDS, METEORS • A METEOROID a lump of rock smaller than an asteroid that gets pulled into Earth’s atmosphere. • METEOR As it travels through the Earth’s atmosphere, friction with particles in the air causes it to burn up. If it is large enough we can see a flash of light from Earth, also called a “SHOOTING STAR” • METEORITE any part of the meteoroid that survives and lands on earth. Large meteorites can leave behind huge holes called craters. COMETS • Chunks of ice, dust and rock that travel in long, oval orbits around the Sun. • Referred to as dirty Snowballs. • As they near the Sun, the heat from the Sun vapourizes the frozen gases and dust, and the solar wind pushes them out creating a long, colourful tail. • The glowing tail can be seen for months. Scale Diagram • http://www.exploratorium.edu/ronh/solar _system/