* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download light years - Physics and Astronomy
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
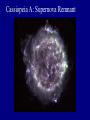
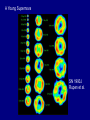
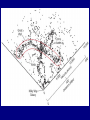
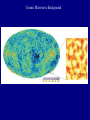
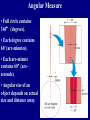
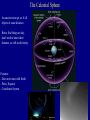
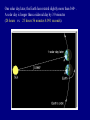
Scales of the Universe Powers of 10 film What conclusions can you draw from this film Continuing A Quick Tour of the Universe (and this course) Cassiopeia A: Supernova Remnant Example Supernova: 1998bw A Young Supernova SN 1993J Rupen et al. 1 kpc Cosmic Microwave Background Clicker Question: If Earth rotated twice as fast as it currently does, but its motion around the sun stayed the same, then which of the following is true: A: the night would be twice as long B: the night would be half as long C: the year would be half as long D: the year would be twice as long E: the length of a day would be unchanged Foundations of Astronomy The Metric System (used by scientists and foreigners) Mass 1 kilogram (kg) = 1000 grams (g) 28 g = 1 ounce If your mass is 220 lbs, it's also 100 kg. We tend to use mass and weight interchangeably, but weight depends on gravity. Distance 1 meter (m) = 100 centimeters (cm) = 39.4 inches (slightly longer than a yard - your professor is 1.8 m in height) 1 cm = 0.39 inches Volume 1 cubic centimeter or 1 cm3 = 0.06 cubic inches (about the size of a sugar cube) Temperature The Celsius Scale: T(oC) = 5/9 [ T(oF) - 32 oF ] so 32 oF = 0 oC 212 oF = 100 oC 68 oF = 20 oC The Kelvin Scale: T(K) = T(oC) + 273 oC "Absolute zero" 0 K = -273 oC Angular Measure 90o 20o 360o, or 360 degrees, in a circle. 1o = 60' or arcminutes 1' = 60" or arcseconds 1" = 1000 mas or milli-arcseconds Angular Measure • Full circle contains 360° (degrees). • Each degree contains 60′ (arc-minutes). • Each arc-minute contains 60″ (arcseconds). • Angular size of an object depends on actual size and distance away. THE QUEST FOR RESOLUTION Resolution = Observing wavelength / Telescope diameter Angular Optical (5000A) Radio (4cm) Resolution Diameter Instrument Diameter Instrument 2mm Eye 140m GBT+ 1¢ 10cm Amateur Telescope 8km VLA-B 1² 2m HST 160km MERLIN 0.²05 100m Interferometer 8200km VLBI 0.²001 Atmosphere gives 1" limit without corrections which are easiest in radio 1 arcmin Jupiter and Io as seen from Earth 1 arcsec 0.05 arcsec 0.001 arcsec Simulated with Galileo photo Scientific Notation (A shorthand way of writing very large and small numbers, which occur often in astronomy). We use powers, or exponents, of 10: 100 1000 1,000,000 10 1 0.1 0.0001 0.007 = 102 (= 10 x 10) = 103 (= 10 x 10 x 10) = 106 = 101 = 100 = 10 -1 = 10 -4 = 7 x 10 -3 Add the exponents 4000 x 0.002 = (4 x 103) x (2 x 10 -3) = 8 x 100 = 8 Scales of your world Think about • How big your car is? • How your house/apartment is? • How big Albuquerque is? • How big the US is? • How far away the farthest place you have travelled is? • How massive a very big man-made object is? In astronomy, we deal with: 1. Vast distances • - Radius of Earth = 6,400 km = 6.4 x 106 m - Distance to Moon =384,000 km = 3.8 x 108 m • • - Distance to Sun = 1.5 x 1011 m = 23,500 Earth radii = 1 Astronomical Unit (AU) - Distance to next nearest star (Proxima Centauri): 270,000 AU = 4.3 "light years" (light year: distance light travels in one year, 9.5 x 1012 km. Speed of light c = 3 x 108 m/sec) • - Size of Milky Way Galaxy: about 100,000 light years • - Distance to Andromeda Galaxy = 2.5 million light years - Distance to nearest cluster of galaxies (Virgo Cluster): 5 x 107 light years 2. Huge masses: - Mass of Earth = 6 x 1024 kg = 6 x 1027 g = 1 MEarth (or 6000 billion billion tons) - Mass of Sun = 2 x 1030 kg = 2 x 1033 g = 1 MSun = 1 "Solar Mass" = 333,000 MEarth - Mass of Milky Way galaxy: more than 1011 MSun - Mass of a typical cluster of galaxies: about 1015 MSun 3. Long ages and times: - Age of Earth and Solar System: 4.5 billion years = 4.5 x 109 years - Lifetime of stars: about 106 - 1010 years -Age of universe: about 1010 years 4. Very high and low temperatures: - An interstellar "molecular cloud": T = 10 K - Center of Sun: T = 1.5 x 107 K Clicker Question: How many stars are there in the observable universe? A: 1012 B: 1022 C: 1032 D: 1042 E: infinite Clicker Question: Distances to nearby stars are measured by: A: bouncing radar signals off them B: using laser beams C: using geometry and parallax measurements D: measuring how long it took a spacecraft to get there and back and assuming a constant velocity. The Sky at Night What do we see? The Moon Planets Perhaps a meteor shower, comet, or other rare event Stars - about 3000 visible Patterns of stars - constellations 88 of them Useful for finding our way around the sky, navigating the oceans Satellites, airplanes, clouds, lightning, light pollution ... The Celestial Sphere An ancient concept, as if all objects at same distance. But to find things on sky, don't need to know their distance, so still useful today. Features: - Does not rotate with Earth - Poles, Equator - Coordinate System The "Solar Day" and the "Sidereal Day" Solar Day How long it takes for the Sun to return to the same position in the sky (24 hours). Sidereal Day How long it takes for the Earth to rotate 360o on its axis. These are not the same! One solar day later, the Earth has rotated slightly more than 360o . A solar day is longer than a sidereal day by 3.9 minutes (24 hours vs. 23 hours 56 minutes 4.091 seconds).