* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monitoring Stellar Magnetic Activity Cycles with SONG
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
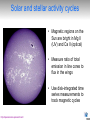
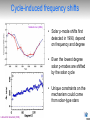
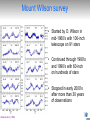
Monitoring Stellar Magnetic Activity Cycles with SONG Travis Metcalfe Solar and stellar activity cycles • Magnetic regions on the Sun are bright in Mg II (UV) and Ca II (optical) • Measure ratio of total emission in line cores to flux in the wings • Use disk-integrated time series measurements to track magnetic cycles http://spacescience.spaceref.com/ Cycle-induced frequency shifts Salabert et al. (2004) • Solar p-mode shifts first detected in 1990, depend on frequency and degree • Even the lowest degree solar p-modes are shifted by the solar cycle • Unique constraints on the mechanism could come from solar-type stars Libbrecht & Woodard (1990) Mount Wilson survey • Started by O. Wilson in mid-1960’s with 100-inch telescope on 91 stars • Continued through 1980’s and 1990’s with 60-inch on hundreds of stars • Stopped in early 2000’s after more than 30 years of observations Baliunas et al. (1995) Lowell survey • 1.1-m telescope close to Flagstaff Arizona, allocate 7 nights/month bright time • Solar observations 3-6x per week, 50 target stars sampled a few nights/mo. • Solar/stellar/comparison all fed to spectrograph through a single fiber Hall & Lockwood (1995) Solar-Stellar spectrograph • Built at NCAR, delivered to Lowell in 1988, regular observations since 1995 • Dedicated to long-term observations of the Sun and Sun-like stars • Example: observations of the “solar twin” 18 Sco show ~7 yr activity cycle Hall, Lockwood & Henry (2007) SMARTS survey • Small telescopes at CTIO now run by a consortium; NCAR is a minor partner • Monitor bright southern asteroseismic targets for stellar activity variations • Example: observations of the exoplanet host star HD 17051 = HR 810 Metcalfe et al. (2009, arXiv:0909.5464) SONG at MLSO






![Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007097773_1-15996a23762c2249db404131f50612f3-150x150.png)