* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download radioactivity PowerPoint Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
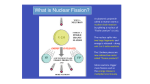
ABC’s of Radiation Howard AAPT 2005 Matis - Albuquerque - [email protected] 1 Howard Matis Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory • • • • • • AAPT 2005 - Albuquerque Howard Matis - [email protected] 2 What is a Nucleus? Quarks determine if proton or neutron • Neutrons • Protons • Protons determine chemical propertiesRatio of neutrons to protons make a nucleus stable or unstable • • • • Examples - Isotopes Uranium-238 (23892U) – • Uranium-235 (23592U) – – • 1 proton, 0 neutrons, mass 1 Deuterium (21D) – • 92 protons, 143 neutrons, mass 235 Hydrogen (11H) – • 92 protons, 146 neutrons, mass 238 1 proton, 1 neutron, mass 2 Tritium (31T) – 1 proton, 2 neutrons, mass 3 • Nuclear Stability • N = # of Neutrons • Z = # of Protons • White are the stable nuclei • For light nuclei, stable nuclei have N=Z • If too many protons, then a proton will turn into a neutron • If too many neutrons, a neutron will turn in a proton • • How Does it Decay? • Alpha - lose an alpha particle (a - helium nucleus) Beta - emit a beta particle (b - electron or anti-electron) Gamma - emit a gamma (g or photon or light particle) • • Alpha Decay • Alpha particle or helium nucleus emitted • Nucleus changes mass by four units and charge by two units – Alpha particle easily stopped – 4 x nucleon mass – +2 Charge – Big • Beta Decay • Beta minus - neutron converts to electron and anti-neutrino • Beta plus - proton converts to a anti-electron and neutrino • Nucleus changes charge but not mass number – Radiation moderately penetrating – +1 charge • Small electron • • Gamma Decay • Nucleus changes energy level - emits gamma ray or photon • Nucleus stays the same – Very penetrating – Very small – Neutral • Penetrating Properties of • Ionizing Radiation • Cosmic Rays Another form of Radiation • Comes from outside the earth Particles from the sun • Star dust - from supernova - exploding stars Consists of protons and neutrons • • Sources of Radiation • Average radiation exposure in the United States - 360 mrem Very location dependent • • • Additional Sources Plane travel • Living at high elevation - Albuquerque has 2x cosmic radiation Soil • Medical x-rays • Occupational exposure • Is radiation bad for you? • Too difficult to directly measure risk of low level • Use high exposure studies to determine radiation damage • Extrapolate from high exposure to low • Model assumes that body does not heal from radiation exposure • Similar to calculating the risk of death from a pin prick by extrapolating from a knife wound • Relative Risk1 in a million fatality • 40 tablespoon peanut butter (aflotoxin) • 2 days in New York City (air quality) • • 3 mrem radiation (cancer) 1 mile on motorcycle (collision) • 300 miles in car (collision) • 10 charbroiled steaks • Smoking 1 cigarette