* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 26 ~ Stars and Galaxies Section 1 ~ Constellations
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Arecibo Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Allen Telescope Array wikipedia , lookup
Lovell Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
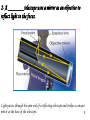
Chapter 26 ~ Stars and Galaxies Section 1 ~ Constellations Chapter 26 Section 1 Before you read - write the reading’s objectives in this space: 1 – _______________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ 2 – _______________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ 3 - ________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ What is a Constellation? __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ •Constellations and the stars that make them up are visible with the unaided eye. 1 What are telescopes used for? ____________________ ._________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ There are two basic types of optical telescopes, what are they? 1- _________________- Uses only lenses to study light. 2 Light passes through the objective lens. The eyepiece then magnifies the image. 2- A ________telescope uses a mirror as an objective to reflect light to the focus. Light passes through the open end of a reflecting telescope and strikes a concave mirror at the base of the telescope. 3 How can you can find the magnifying power (Mp) of a telescope? ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Formula: 4 What would the magnifying power for a telescope with a focal length of 3,000mm and an eyepiece with a focal length of 40mm be? Formula: Plug in and solve: 5 If the focal length of a telescopes objective is 800mm and the magnifying power of the telescope is 40 times, what is the focal length of the eye piece? Formula to use: Plug in and solve: 6 The most recent innovations in optical telescopes involve active and adaptive optics. _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ What does adaptive optics do? _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 7 What is a radio telescope? __________________________________________ __________________________________________ Radio waves have long wavelengths, a radio telescope must be built with a very large objective, usually some form of dish antenna. Astronomers often build several radio telescopes close together and connect them to form one large telescope. 8 Hubble Space Telescope Even using active and adaptive optics, the atmosphere limits what Earth-based telescopes can achieve. For this reason, astronomers use space telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope. How Hubble Sees (2 min) Hubble Repair (1 min) What is a light-year? __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ 9 What is a spectroscope? ________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Can you think of a time when we did something similar? **This can tell astronomers a great deal about a star. For example, they can determine its chemical composition, its surface temperature, and whether it is moving away from or toward Earth. 10 What does a spectroscope do? A spectroscope helps us find out what stars are made of. It disperses, or separates, white light from a star into a very wide spectrum of colors — much wider than a normal prism does. When spread very wide, black lines appear in the spectrum. The first scientists to observe these lines wondered why they were there and what they meant. It turns out that particular elements in the star created particular patterns of lines. Once scientists knew the element responsible for a certain pattern, they knew which elements were present in the star. This was a revolutionary discovery. Section Check 1 Question 1 A refracting telescope uses a _______ as an objective. A. mirror B. wave C. convex lens D. laser 11 Section Check 1 Question 2 What does a spectroscope do? 12 Section Check 1 Question 3 What is the distance that light travels in one year? A. 15 million km B. 9.5 trillion km C. 12 billion km D. 2 million km 13