* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of the Universe
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
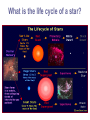
What is a galaxy? • A collections of billions of stars held together by gravity • There are billions of galaxies • Galaxies make up the universe What is the name our galaxy? • Milky Way- Why is it called that? • Because we are on an outer arm of the spiral (looks like a pin wheel) when you look into it, it looks like a milky cloud. What is a star? A ball of gases held together by gravity which produces large amounts of energy. How do stars produce energy? Stars produce energy by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, What is luminosity? Measure of how bright a star would be compared to the sun, if they were both the same distance away from an observer. What is apparent brightness? • The apparent brightness is what we observe when we look at stars. • The apparent brightness depends on: – How close it is – How bright it actually is. Star types • Main sequence – Average size – As temperature increases, so does luminosity • Giant stars – Large, bright, cool stars – Red, orange or yellow in color – 10 or more times brighter then the sun • Super giants – High luminosity, high temperature – 100 to 1000 times bigger then the sun – Later in life; already a main sequence star • White dwarfs – Small, dim and hot stars – Last shinning stage of a star • Black dwarfs – A white dwarf that cools and no longer gives off energy “dead star” Using the Reference tables How would you classify our sun? A main sequence star with a yellow color and average size, and about 5,000-6,000 degrees in temperature. What is the life cycle of a star? What determines the stages of star development? The original mass of the star determines its life cycle and how long it lasts.