* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Definitions
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Epoch (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
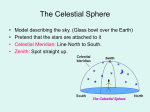
CONSTELLATIONS • Constellation: formation of stars perceived as a figure or design. – 88 recognized groups named after characters from classical mythology and various common animals and objects. • Asterism: star patterns that are not constellations. They may be contained within single constellations or between multiple constellations. • Ecliptic: the great circle representing the apparent annual path of the sun; the plane of the Earth's orbit around the sun; makes an angle of about 23 degrees with the equator; "all of the planets rotate the sun in approximately the same ecliptic" • Declination: one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system. Comparable to Latitude. Expressed as an angle with respect to the celestial equator. • Right Ascension: a celestial longitude measured in the direction of the Earth’s rotation. The notation adopted for right ascension is in terms of hours and minutes with 24 hours representing the full circle. • Circumpolar star: a star that as viewed from a given latitude on Earth, never disappears below the horizon, due to its proximity to one of the celestial poles. Visible for the entire night (and throughout the day if it wasn’t for the sun’s glare) every night of the year. The North Polar Sky declination 90° to 50° • Polaris lies less than 1° from the north celestial pole • For observers in the Northern Hemisphere the stars are circumpolar • The viewer’s latitude will determine how much of the sky is circumpolar The South Pole Sky -50° to -90° • There is no southern equivalent of Polaris • Many of these stars are circumpolar for observers in the Southern Hemisphere. Equatorial Sky (Chart 1: 21h to 3h contains 0h line of right ascension) • Observed during evenings in Sept, Oct and Nov • Contains the Vernal equinox in Pisces (the Sun will pass through here in late March) Equatorial Sky (Chart 2: 15h to 21h) • Observed during evenings in June, July and August • Contains the point where the sun reaches its most southerly declination in Sagittarius around Dec 21 Equatorial Sky (Chart 3: 9h to 15h) • Observed on evenings in March, April and May. • Contains the Autumn equinox in Virgo around Sept 21 Equatorial Sky (Chart 4: 3h to 9h) • Observed during evenings in December, January and February • Contains the point at which the Sun is furthest north on the border of Taurus and Gemini around June 21