* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download observingnebulaeclusters-1
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
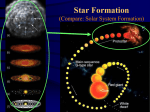
Spring 2012 Astronomy Course Mississippi Valley Night Sky Conservation The Sky Around Us Program developed by Mississippi Valley Conservation Authority Royal Astronomical Society of Canada Ottawa Astronomy Friends Instructors: Pat Browne Stephen Collie Rick Scholes Earth Centered Universe software for illustrations – courtesy David Lane Observing nebulousity In Clusters in the western sky Past the near objects, the planets, and beyond the double and variable stars is a special realm. Here are the star clusters, gas clouds and star nurseries. Open Clusters looking West (setting) ( Spring time Northern Hemisphere) WHERE Locating Nebulae in Clusters Observing nebulousity around individual stars WHEN Are they Visible? Observing (Winter) nebula in the Spring Western Sky – early evening! WHAT Types of Nebulae Open Clusters and their Nebulae – Reflection Nebulae Groups of Stars embedded within a hydrogen cloud – Emission Nebula WHERE: > 500 light years (M42 is located at a distance of 1344 ± 20 light years and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth.) This is much further out than… Nearest and Brightest stars 5-15 light years Consider: Lecture 1,II – Stars on the celestial sphere < 500 light years Famous Examples: Pleiades – Reflection Nebula M42 trapezium – Emission Nebula Levy 1 (NGC 1931) Reflection/Emission Nebula M78 – Reflection Nebula Orion Nebula M42 - Closeup "Flying" into the Orion Nebula This animation was produced by Walt Feimer in the Astronomy Visualization Laboratory at the Space Telescope Science Institute. It begins with a "backyard" view of the sky around the constellation Orion (by Skip Westphal, STScI) and a more detailed view of the Orion Nebula, M42 . Images taken with the 4-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. A spectacular cloud of gas surrounds several very hot stars in the star cluster deep within the nebula. The nebula's constituent gases include hydrogen, helium, oxygen, carbon, neon, nitrogen, sulphur, argon, and chlorine; the density of these gases is above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Telescope (C.R. O'Dell, Rice University) provides a more detailed view of the Nebula. The final sequence, from details of the HST image, show several protoplanetary disks or "proplyds" and finally a single dark disk surrounding a central star. Reflection Nebula in Young Star Clusters For most purposes it can be assumed that the stars in a given cluster formed simultaneously from the same parent cloud of gas and dust. When comparing star clusters, we oftennote the density of stars, their age and their chemical composition (as revealed by their spectra ). Young Star clusters also often exhibit nebulous trails of gas and dust which emanate from members that are still in the process of becoming stars! Also, those young stars often continue to radiate and reflect off of the dusty lanes that mark their birth into the cluster. Photographically, and with spectral analysis, we can see that the blue nebulousity is reflected light off of the hot young stars The red nebulousity is due to emission of light emanating from hot hydrogen clouds… M78 is the brightest diffuse reflection nebula of a group of nebulae that include NGC 2064, NGC 2067 and NGC 2071. This group belongs to the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex and is about 1,600 light years distant from Earth. M78 is easily found in smal ltelescopes as a hazy patch and involves two stars of 10th magnitude. responsible for making the cloud of dust in M78 visible by reflecting their light. Observe: Catalogue Name ------------------------------M42 Great Orion Nebula – Emission and Reflection M78 Reflection Nebula (Orion) M45 – Pleiades (the 7 sisters) - the stars dominate Levy 1 – Auriga NGC 1931 The nebulousity dominates… reflected off of gas and dust Levy 1 NGC 1931 M78 M42 M45