* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download February 6
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Axial precession wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
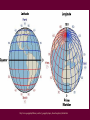
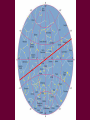
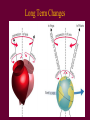
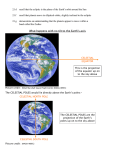
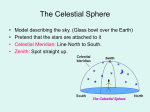
Survey of the Universe Tom Burbine [email protected] All stars rotate around Polaris throughout the evening http://www.flickr.com/photos/odalaigh/1482685365/ Polaris • Polaris' altitude, or height above the horizon, is equal to an observer's latitude. http://www.geographyalltheway.com/ks3_geography/maps_atlases/longitude_latitude.htm Celestial Coordinates • Coordinates on the celestial sphere • Right ascension – east-west position (hours, minutes, seconds) • Declination – north-south position (degrees) http://www.oneminuteastronomer.com/3924/sky-coordinates/ Zodiac • The zodiac is an imaginary belt in the heavens extending approximately 8 degrees on either side of the Sun's apparent path (the ecliptic), that includes the apparent paths of the Moon and the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Question: • Why do all the planets seem to follow the same path? Answer: • The planets, the Earth, and the Sun all tend to fall in the same plane called the ecliptic Celestial Equator • Extension of the Earth’s equator into the Celestial Sphere Question: • Why is the path of the constellations on the zodiac not on the celestial equator? Answer: • The rotation axis of the Earth is inclined with respect to the ecliptic Long Term Changes Precession • Earth precesses like a top • Precession - phenomenon by which the axis of a spinning object (e.g. a part of a gyroscope) "wobbles" when a torque is applied to it Forces • For a top, the force is gravity, which is trying to pull the top down • For the Earth, the forces are due to the pull of the Sun and Moon, which is trying to align the Earth’s axis with the ecliptic Because of precession • The position of a star that corresponds to the North Celestial Pole changes What causes seasons? • The tilt of the Earth’s axis relative to the ecliptic Seasons Solstices • Summer Solstice –June 21 – Northern Hemisphere receives its most direct sunlight • Winter Solstice – December 21 – Northern Hemisphere receives its least direct sunlight Equinoxes • Sun shines equally on both hemispheres • Spring Equinox – March 21 – Northern Hemisphere goes from slightly tipped away from the Sun to slightly tipped towards • Fall Equinox – September 21 - Northern Hemisphere goes from slightly tipped toward from the Sun to slightly tipped away Why does the orbital difference not matter? Reasons • There is only a 3% difference in the distance from the Earth to the Sun at its farthest and closest point • The Earth is actually closer to the Sun in the winter than in the summer Seasons • Everybody should watch this video on why we have seasons • http://www.learner.org/resources/series28.html?p op=yes&pid=9# Any Questions?