* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CO 2 Cycle
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
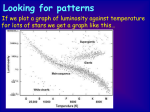
Science News Signs of Flowing Water on Mars…TODAY! Bright new deposits seen in NASA images of two gullies on Mars suggest liquid water carried sediment in the past several years…The atmosphere on Mars is so thin that liquid water cannot persist at the surface. However, researchers propose that water could remain liquid long enough, after breaking out from an underground source, to carry debris before totally evaporating and freezing. About the Final • • • • • Date: Thursday, December 14, 2006 Time: 12:00 Noon to 2:00 PM Place: Watanabe 112 30% of your grade 75 multiple-choice questions – 25 from midterm and quiz 7 to 12 – 50 new questions Review for Final • The followings are important areas from each chapter that I will draw my final exam questions from… • This is a general guideline only. • Do not be surprised if there are few questions not mentioned here… Chapter 7 Earth and the Terrestrial Worlds • Internal Structure • Atmosphere • What makes the Earth hospitable to life? – CO2 cycle – Greenhouse effect • Global Warming? Internal Structure of the Terrestrial Planets • General Structure of the Terrestrial Planets – What’s at the core – What’s at the top – Tectonic Atmosphere • How does Earth’s atmosphere differ from other terrestrial planets? • What factors determine the composition of terrestrial planets atmosphere? • What are the distinguishing properties of Earth that help to make Earth Habitable? – Mass – Magnetic field – Life • What happened on Mars? • What happened on Venus? CO2 Cycle • • • • What is the CO2 cycle? How does the CO2 cycle work? Where are the CO2 on Earth? How does CO2 cycle regulates Earth’s surface temperature? Greenhouse Effect • • • • What is greenhouse effect? How does greenhouse effect work? – Sunlight heats the surface of the Earth during the day. – The Earth re-radiates the heat back into space during the night. – Greenhouse gases prevent the heat (thermal infrared light emitted by the warm surface) from escaping into space. What are the most important greenhouse gases? 1. Water vapor (not liquid water or ice). 2. CO2 Global warming Chapter 8 Jovian Planet System • Internal Structure • Surface Features – The Giant Red Spot – The Bands of Jupiter Chapter 10 The Sun • General Structure • Chemical composition of the Sun • Source of Solar Energy – What’s going on in the core of the Sun? – How does the energy generated in the core get to us on Earth? In what form? Sunspots and Solar Cycle • • • • What are sunspots? What is the sunspot cycle? How does it work? What do the solar cycle and solar activities got to do with us? Age and Lifetime of the Sun • How old is the Sun now? • How much longer is the Sun going to live? • What’s going to happen to the Sun when and after it dies? Chapter 11 Surveying the Stars • Basic Properties of Stars – – – – Mass Luminosity Surface Temperature and Spectral Type Size • How do we measure the properties of stars? – Distance – Size – Mass • Know your H-R Diagram! Apparent Brightness and Luminosity • • • • What is apparent brightness? What is luminosity? What is the luminosity-distance relation? How do we use the luminosity-distance relation? – Apparent brightness + Distance → Luminosity! – Apparent brightness + Luminosity → Distance! Know Your HR Diagram! • What’s in the HR diagram? – – – – Temperature and Spectral Type Luminosity Mass Size • How are they arranged? – Where are the hot stars in the HR diagram? – Where are the big stars? – Where are the bright (high luminosity) stars? • How are stars grouped in the HR diagram? – Main Sequence stars – Red Giants and Supergiants – White dwarfs Know Your Stars • What is a main sequence (MS) star? – What’s going on in the core of the MS stars? – How’s mass related to their size, temperature, luminosity, and lifetime? • What are red giants and supergiants? – What’s going on in the core of the giants? – What’s going on around the core? – What do they look like from the outside? • Stellar Classification – Spectral Type: OBAFGKM – Luminosity Class: I, II, III, IV, V Star Clusters • Open and Globular Clusters – Where are they located? – How are they different in • Number of stars • Spatial distribution • How do we determine the age of star clusters Chapter 12 Star Stuff • Evolution of Low-Mass Stars – What’s the nuclear fusion process during MS stage? – What’s going on inside during the giant stage? – When do they stop fusion? – Why do they stop fusion? – How do they die? – What becomes of the low-mass stars after they die? High-Mass Stars • Evolution of High-Mass Stars – What’s the nuclear fusion process during the MS stage? – What’s the inside looks like when it’s a giant? – Why does fusion stop? – Why does fusion stop? – How do they end their life? – What becomes of high-mass stars after they die? Chapter 13 The Dead Stars • What keeps the dead stars from collapsing? – How does degenerate pressure work? • White Dwarfs – What’s inside the white dwarfs? – White dwarf supernovae – how do you make one? • Chandrasekhar Limit – How does white dwarf supernova differs from massive-star supernova – Why is white dwarf supernova important in cosmology? Neutron Stars • How do you make a neutron star? • What do neutron stars look like? – Fast rotation – Strong magnetic field – Hot! (initially) – X-ray – Pulsar – How do we find them? Black Holes • What makes a black hole? – Mass within the event horizon – Schwarzschild radius • Light cannot escape black hole – Not because of the gravitational force acting on the photons – But because strong gravity bend the path (spacetime) of the photon backward Is there a black hole at the center of the Milky Way? • What’s at the center of the milky way? • How can we tell if it is a black hole? • What observational evidence we have? Chapter 15 A Universe of Galaxies • Galaxy Classification • Spiral or Elliptical? – What conditions in the protogalactic clouds determine whether it’s a spiral or elliptical? • How do we measure distance to galaxies? What method is good for – nearby stars? – Within the galaxy? – Nearby galaxies – Far-away galaxies? – Very far-away galaxies? Universal Expansion • What did Edwin Hubble find about galaxies • Implications of Hubble’s discovery – Expansion of the universe – Age of the Universe – Fate of the Universe Fate of the Universe • What’s the possible fate of the universe? • What’s the most important property that determines the fate of the universe? – How much mass do we have? – Dark matter – Dark Energy